一个App中如果能有优秀的动画效果,能让App看起来显得更加高大上。此篇我们就来介绍一下Flutter中Animation体系。
我们先来一个简单的例子,来实现透明度渐变动画:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
2 @override
3 State createState() {
4 return _FadeInDemoState();
5 }
6}
7
8class _FadeInDemoState extends State {
9 double opacity = 0.0;
10
11 @override
12 Widget build(BuildContext context) {
13 return Column(
14 children: <Widget>[
15 MaterialButton(
16 child: Text(
17 "Click Me",
18 style: TextStyle(color: Colors.blueAccent),
19 ),
20 onPressed: () => setState(() {
21 opacity = 1;
22 }),
23 ),
24 AnimatedOpacity(
25 duration: const Duration(seconds: 2),
26 opacity: opacity,
27 child: Text('Flutter Animation Demo01')
28 )
29 ],
30 );
31 }
32}
33
这里我们借助于AnimatedOpacity来实现渐变:我们通过点击按钮来触发动画效果,如下图所示。

我们来总结一下实现步骤:
- 实现AnimatedOpacity来包裹需要实现透明度渐变动画的Widget,并指定duration和opacity参数。这俩参数也好理解:duration自然是动画时间,opacity表示透明度(取值范围为0~1,0表示透明)
- 触发动画:通过setState()方法,我们可以直接指定opacity的最终值(为1,即完全显示)。因为所谓的动画,肯定是有起始状态和结束状态,然后在指定的动画时间内慢慢发生变化。
2.使用AnimatedContainer来实现其他属性变化的动画.
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
2 @override
3 State createState() {
4 return _AnimatedContainerDemoState();
5 }
6 }
7
8 class _AnimatedContainerDemoState extends State<AnimatedContainerDemo> {
9 Color color;
10 double borderRadius;
11 double margin;
12
13 double randomBorderRadius() {
14 return Random().nextDouble() * 64;
15 }
16
17 double randomMargin() {
18 return Random().nextDouble() * 64;
19 }
20
21 Color randomColor() {
22 return Color(0xFFFFFFFF & Random().nextInt(0xFFFFFFFF));
23 }
24
25 void change() {
26 setState(() {
27 initState();
28 });
29 }
30
31 @override
32 void initState() {
33 color = randomColor();
34 borderRadius = randomBorderRadius();
35 margin = randomMargin();
36 }
37
38 @override
39 Widget build(BuildContext context) {
40 return Scaffold(
41 body: Center(
42 child: Column(
43 children: <Widget>[
44 SizedBox(
45 width: 128,
46 height: 128,
47 child: AnimatedContainer(
48 curve: Curves.easeInOutBack,
49 duration: const Duration(milliseconds: 400),
50 margin: EdgeInsets.all(margin),
51 decoration: BoxDecoration(
52 color: color,
53 borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(borderRadius),
54 ),
55 ),
56 ),
57 MaterialButton(
58 color: Theme.of(context).primaryColor,
59 child: Text(
60 'change',
61 style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),
62 ),
63 onPressed: () => change(),
64 )
65 ],
66 ),
67 ),
68 );
69 }
70 }
71
运行效果如下:
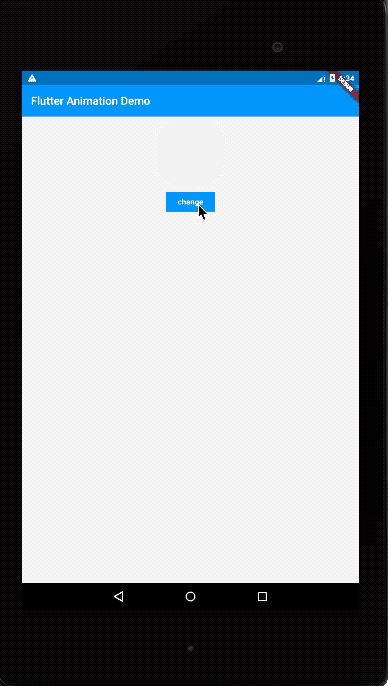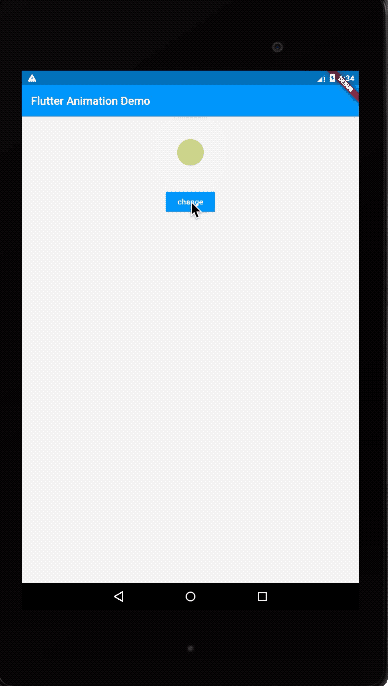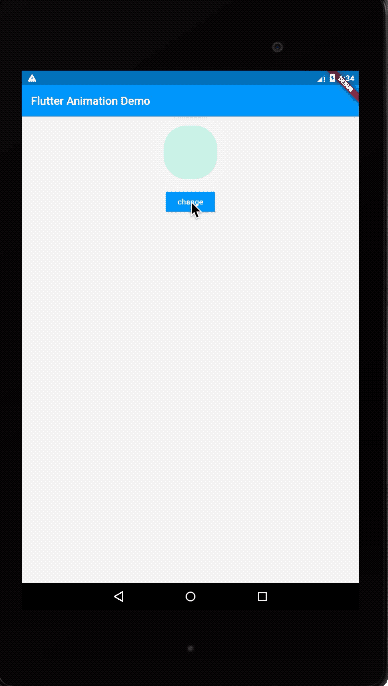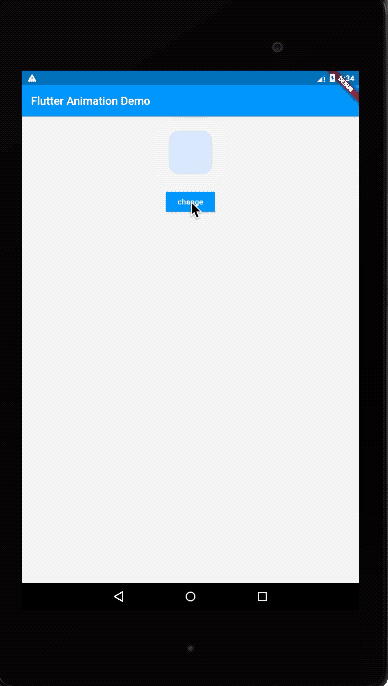
我们这次同时修改了margin、color以及borderRadius三个属性。AnimatedContainer的使用思路和AnimatedOpacity类似:
- 包裹子widget,指定duration及相关属性参数
- 在setState方法中指定属性的动画终止状态
实际上我们刚刚介绍的两种实现方式被称之为隐式动画(implicit animation),可以理解成对于Animation子系统进行了一层封装,方便我们开发者使用。下面我们正式来介绍Animation子系统的重要组成类:
3.Animation类:通过这个类,我们可以知道当前的动画值(animation.value)以及当前的状态(通过设置对应的监听listener),但是对于屏幕上如何显示、widget如何渲染,它是不知道的,换句话说也不是它所关心的,这点从软件设计上耦合性也更低。其次,从代码角度上,它是一个抽象类:

4.AnimationController类。

从类本身上看,它是继承自Animation类的,并且泛型类型为double。从作用上来看,我们可以通过AnimationController来指定动画时长,以及它提供的forward()、reverse()方法来触发动画的执行。
5.CurvedAnimation类:同样继承自Animation类,并且泛型类型为double。它主要用来描述非线性变化的动画,有点类似Android中的属性动画的插值器。

6.Tween类.

从类的层次结构上,它有所不同,不再是继承自Animation,而是继承自Animatable。它主要用来指定起始状态和终止状态的。
好,我们已经对这四个类有了一定的了解,下面我们就从实例来看看他们是如何结合在一起使用的。
7.实例一:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
2 @override
3 State createState() => _LogoState();
4}
5
6class _LogoState extends State with SingleTickerProviderStateMixin {
7
8 // 注释1:这里已经出现了我们前面提到的Animation和AnimationController类
9 Animation<double> animation;
10 AnimationController controller;
11
12 @override
13 void initState() {
14 super.initState();
15 // 注释2:
16 // 在构造一个AnimationController对象时,我们需要传递两个参数
17 // vsync:主要为了防止一些超出屏幕之外的动画而导致的不必要的资源消耗。我们这里就传递
18 // this,除此之外,我们还需要使用with关键字来接入SingleTickerProviderStateMixin类型
19 // duration:指定动画时长
20 controller =
21 AnimationController(vsync: this, duration: const Duration(seconds: 2));
22
23 // 注释3: 通过Tween对象来指定起始值和终止值,并且通过animate方法返回一个Animation对象,
24 // 并且设置了监听,最后在监听回调中调用setState(),从而刷新页面
25 animation = Tween<double>(begin: 0, end: 300).animate(controller)
26 ..addListener(() {
27 setState(() {});
28 });
29
30 // 注释4: 启动动画
31 controller.forward();
32 }
33
34 @override
35 Widget build(BuildContext context) {
36 return Center(
37 child: Container(
38 margin: EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 10),
39 // 注释5:通过Animation对象类获取对应的变化值
40 height: animation.value,
41 width: animation.value,
42 child: FlutterLogo(),
43 ),
44 );
45 }
46
47 @override
48 void dispose() {
49 // 注释6:对controller解注册
50 controller.dispose();
51 super.dispose();
52 }
53}
54
运行效果如图所示:

这里涉及到了两个Dart语言本身的知识点:mixin和..。mixin这里推荐一篇medium上的文章:https://medium.com/flutter-community/dart-what-are-mixins-3a72344011f3;而..很简单,它就是为了方便链式调用。我们可以看下前面addListener()方法,方法本身返回的void类型,但是我们最终却返回了一个Animation类型的对象。这其中就是..起到的作用,它可以使得方法返回调用这个方法的对象本身。
8.使用AnimatedWidget来重构上面的代码:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
2 @override
3 State createState() => _LogoState();
4}
5
6class _LogoState extends State with SingleTickerProviderStateMixin {
7 Animation<double> animation;
8 AnimationController controller;
9
10 @override
11 void initState() {
12 super.initState();
13 controller =
14 AnimationController(vsync: this, duration: const Duration(seconds: 2));
15 animation = Tween<double>(begin: 0, end: 300).animate(controller)
16 ..addStatusListener((status) {
17 if (status == AnimationStatus.completed) {
18 controller.reverse();
19 } else if (status == AnimationStatus.dismissed) {
20 controller.forward();
21 }
22
23 print('$status');
24 });
25
26 controller.forward();
27 }
28
29 @override
30 Widget build(BuildContext context) {
31 return AnimatedLogo(animation: animation);
32 }
33
34 @override
35 void dispose() {
36 controller.dispose();
37 super.dispose();
38 }
39}
40
41
42class AnimatedLogo extends AnimatedWidget {
43 AnimatedLogo({Key key, Animation<double> animation})
44 : super(key: key, listenable: animation);
45
46 @override
47 Widget build(BuildContext context) {
48 final animation = listenable as Animation;
49 return Center(
50 child: Container(
51 margin: EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 10),
52 height: animation.value,
53 width: animation.value,
54 child: FlutterLogo(),
55 ),
56 );
57 }
58}
59
先看效果:

大部分代码是和之前的例子是一样的,不同的是:
- 使用AnimatedWidget,并且Animation对象作为参数传递进来
- 省略了在addListener的回调里调用setState方法来触发页面刷新
这样写的好处:
- 省去了需要调用setState的重复代码
- 使得程序耦合性更低。试想一下,我们的App中有多处都需要实现Logo的resize动画,这个时候我们只需要在使用处定义Animation的描述,最后都使用这里的AnimatedLogo。这样做就使得Widget和Animation的描述进行分离。
我们可以去看一下AnimatedWidget类的源码:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
2 /// Creates a widget that rebuilds when the given listenable changes.
3 ///
4 /// The [listenable] argument is required.
5 const AnimatedWidget({
6 Key key,
7 @required this.listenable,
8 }) : assert(listenable != null),
9 super(key: key);
10
11 /// The [Listenable] to which this widget is listening.
12 ///
13 /// Commonly an [Animation] or a [ChangeNotifier].
14 final Listenable listenable;
15
16 /// Override this method to build widgets that depend on the state of the
17 /// listenable (e.g., the current value of the animation).
18 @protected
19 Widget build(BuildContext context);
20
21 /// Subclasses typically do not override this method.
22 @override
23 _AnimatedState createState() => _AnimatedState();
24
25 @override
26 void debugFillProperties(DiagnosticPropertiesBuilder properties) {
27 super.debugFillProperties(properties);
28 properties.add(DiagnosticsProperty<Listenable>('animation', listenable));
29 }
30}
31
32class _AnimatedState extends State<AnimatedWidget> {
33 @override
34 void initState() {
35 super.initState();
36 widget.listenable.addListener(_handleChange);
37 }
38
39 @override
40 void didUpdateWidget(AnimatedWidget oldWidget) {
41 super.didUpdateWidget(oldWidget);
42 if (widget.listenable != oldWidget.listenable) {
43 oldWidget.listenable.removeListener(_handleChange);
44 widget.listenable.addListener(_handleChange);
45 }
46 }
47
48 @override
49 void dispose() {
50 widget.listenable.removeListener(_handleChange);
51 super.dispose();
52 }
53
54 void _handleChange() {
55 setState(() {
56 // The listenable's state is our build state, and it changed already.
57 });
58 }
59
60 @override
61 Widget build(BuildContext context) => widget.build(context);
62}
63
可以看到在initState方法里,添加了动画监听,回调的执行逻辑为_handleChange()方法,而_handleChange()的实现就是调用了setState方法,这点和我们之前在第7条中例子的写法一样。也就是说,AnimatedWidget只是做了一层封装而已。
9.使用AnimatedBuilder进一步重构上面的代码:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
2 @override
3 State createState() => _LogoState();
4}
5
6class _LogoState extends State with SingleTickerProviderStateMixin {
7 Animation<double> animation;
8 AnimationController controller;
9
10 @override
11 void initState() {
12 super.initState();
13 controller =
14 AnimationController(vsync: this, duration: const Duration(seconds: 2));
15 animation = Tween<double>(begin: 0, end: 300).animate(controller);
16 controller.forward();
17 }
18
19 @override
20 Widget build(BuildContext context) {
21 return GrowTransition(child: LogoWidget(), animation: animation);
22 }
23
24 @override
25 void dispose() {
26 controller.dispose();
27 super.dispose();
28 }
29}
30
31
32class LogoWidget extends StatelessWidget {
33 @override
34 Widget build(BuildContext context) {
35 return Container(
36 margin: EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 10),
37 child: FlutterLogo(),
38 );
39 }
40}
41
42class GrowTransition extends StatelessWidget {
43 GrowTransition({this.child, this.animation});
44
45 final Widget child;
46 final Animation<double> animation;
47
48 @override
49 Widget build(BuildContext context) {
50 return Center(
51 child: AnimatedBuilder(
52 animation: animation,
53 builder: (context, child) => Container(
54 height: animation.value,
55 width: animation.value,
56 child: child,
57 ),
58 child: child),
59 );
60 }
61}
62
我们可以在任意地方使用这里GrowTransition,代码进行进一步分离。
10.使用Transition。
Flutter还为我们提供一些封装好的Transition,方便我们实现动画效果,下面我们就以ScaleTransition为例,说明如何去使用这些Transition。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
2 @override
3 State createState() => _LogoState();
4}
5
6class _LogoState extends State with SingleTickerProviderStateMixin {
7 Animation<double> animation;
8 AnimationController controller;
9
10 @override
11 void initState() {
12 super.initState();
13
14 controller =
15 AnimationController(vsync: this, duration: const Duration(seconds: 2));
16 animation = Tween<double>(begin: 0, end: 10).animate(controller);
17 controller.forward();
18 }
19
20 @override
21 Widget build(BuildContext context) {
22 return Center(
23 child: ScaleTransition(
24 scale: animation,
25 child: FlutterLogo(),
26 ));
27 }
28
29 @override
30 void dispose() {
31 controller.dispose();
32 super.dispose();
33 }
34}
35
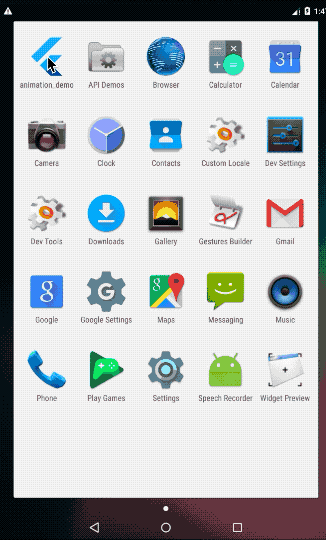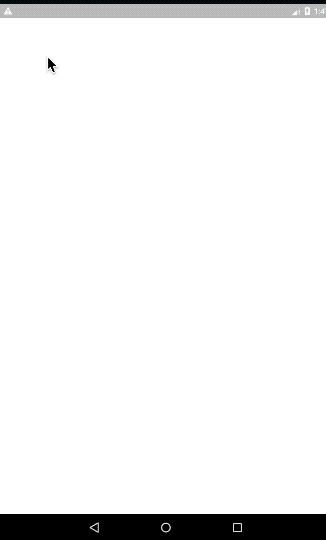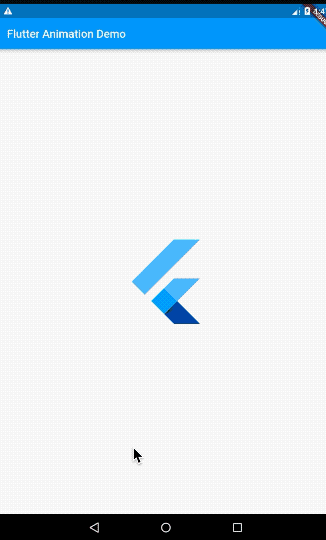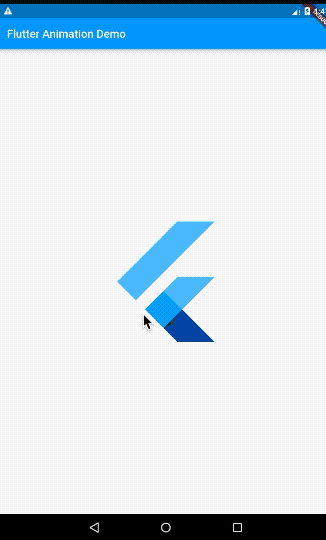
ScaleTransition在使用时需要指定两个参数:
- scale: 就是一个Animation对象
- child: 需要实现缩放动画的widget
最后再注意一下Tween中指定的值所表示的含义,它表示的倍数。比如我们这里end填入了10,表示动画结束状态为放大10倍。我们可以通过ScaleTransition的源码来说服大家:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
2 /// Creates a scale transition.
3 ///
4 /// The [scale] argument must not be null. The [alignment] argument defaults
5 /// to [Alignment.center].
6 const ScaleTransition({
7 Key key,
8 @required Animation<double> scale,
9 this.alignment = Alignment.center,
10 this.child,
11 }) : assert(scale != null),
12 super(key: key, listenable: scale);
13
14 /// The animation that controls the scale of the child.
15 ///
16 /// If the current value of the scale animation is v, the child will be
17 /// painted v times its normal size.
18 Animation<double> get scale => listenable;
19
20 /// The alignment of the origin of the coordinate system in which the scale
21 /// takes place, relative to the size of the box.
22 ///
23 /// For example, to set the origin of the scale to bottom middle, you can use
24 /// an alignment of (0.0, 1.0).
25 final Alignment alignment;
26
27 /// The widget below this widget in the tree.
28 ///
29 /// {@macro flutter.widgets.child}
30 final Widget child;
31
32 @override
33 Widget build(BuildContext context) {
34 final double scaleValue = scale.value;
35 final Matrix4 transform = Matrix4.identity()
36 ..scale(scaleValue, scaleValue, 1.0);
37 return Transform(
38 transform: transform,
39 alignment: alignment,
40 child: child,
41 );
42 }
43}
44
可以看到,ScaleTransition也是继承自我们前面已经介绍过的AnimatedWidget,然后重点关注build()方法里,用到了Matrix4矩阵,这里的scale.value实际上就是Animation.value,而Matrix4.identity()..scale(),它的三个参数分别表示在x轴、y轴以及z轴上缩放的倍数。
与ScaleTransition类似的还有SlideTransition、RotationTransition等等,读者可以自己去尝试一下,这里就不在一一赘述了。
