一、队列概述
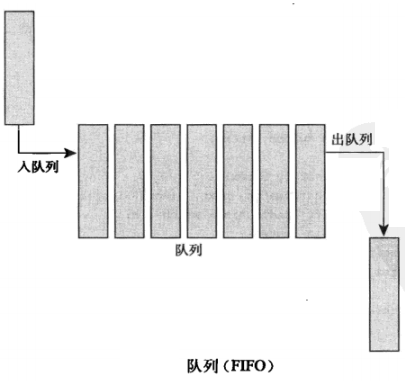
- 任何操作系统内核都少不了一种编程模型:生产者和消费者。在该模式中,生产者创建数据(比如说需要读取的错误信息或者需要处理的网络包),而消费者则反过来,读取消息和处理包,或者以其他方式消费这些数据。实现该模型的最简单的方式无非是使用队列。生产者将数据推进 队列,然后消费者从队列中摘取数据。消费者获取数据的順序和推入队列的顺序一致。也就是说,第一个进队列的数据一定是第一个离开队列的。也正是这个原因,队列也称为FIFO。顾名思义,FIFO就是先进先出的缩写
- 下图是一个标准队列的例子
二、Linux内核队列概述(kfifo)
- Linux内核通用队列实现称为kfifo
- 相关声明在文件<include/kfifo.h>中,相关定义在<kernel/kfifo.c>中
struct kfifo
以下代码来自:Linux2.6.22/include/kfifo.h
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2 unsigned char *buffer; /* the buffer holding the data */
3 unsigned int size; /* the size of the allocated buffer */
4 unsigned int in; /* data is added at offset (in % size) */
5 unsigned int out; /* data is extracted from off. (out % size) */
6 spinlock_t *lock; /* protects concurrent modifications */
7};
8enqueue、dequeue
- Linux提供了两个主要操作:enqueue(入队列)、dequeue(出队列)
入口偏移、出口偏移
kfifo对象维护了两个偏移量:入口偏移和出口偏移
入口偏移是指下一次入队列时的位置
- 出口偏移是指下一次出队列时的位置
出口偏移总是小于等于入口偏移,否则无意义,因为那样说明要出队列的元素根本还没有入队列
三、创建队列
- **备注:**kfifo_init和kfifo_alloc的size必须是2的幂
创建队列并分配缓冲区(kfifo_init)
该函数创建并初始化一个kfifo对象,其使用buffer指向的size字节大小的内存。在kfifo_alloc中会被调用
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2 * kfifo_init - allocates a new FIFO using a preallocated buffer
3 * @buffer: the preallocated buffer to be used.
4 * @size: the size of the internal buffer, this have to be a power of 2.
5 * @gfp_mask: get_free_pages mask, passed to kmalloc()
6 * @lock: the lock to be used to protect the fifo buffer
7 *
8 * Do NOT pass the kfifo to kfifo_free() after use! Simply free the
9 * &struct kfifo with kfree().
10 */
11struct kfifo *kfifo_init(unsigned char *buffer, unsigned int size,
12 gfp_t gfp_mask, spinlock_t *lock)
13{
14 struct kfifo *fifo;
15
16 /* size must be a power of 2 */
17 BUG_ON(size & (size - 1));
18
19 fifo = kmalloc(sizeof(struct kfifo), gfp_mask);
20 if (!fifo)
21 return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
22
23 fifo->buffer = buffer;
24 fifo->size = size;
25 fifo->in = fifo->out = 0;
26 fifo->lock = lock;
27
28 return fifo;
29}
30EXPORT_SYMBOL(kfifo_init);
31动态创建(kfifo_alloc)
参数:
size:创建的大小
- gfp_mask:使用此参数标识分配队列(在后面讨论内存分配时会介绍)
返回值:返回创建的队列
kfifo_alooc()动态创建的队列需要使用kfifo_free来释放(kfifo_free见下)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
2 * kfifo_alloc - allocates a new FIFO and its internal buffer
3 * @size: the size of the internal buffer to be allocated.
4 * @gfp_mask: get_free_pages mask, passed to kmalloc()
5 * @lock: the lock to be used to protect the fifo buffer
6 *
7 * The size will be rounded-up to a power of 2.
8 */
9struct kfifo *kfifo_alloc(unsigned int size, gfp_t gfp_mask, spinlock_t *lock)
10{
11 unsigned char *buffer;
12 struct kfifo *ret;
13
14 /*
15 * round up to the next power of 2, since our 'let the indices
16 * wrap' tachnique works only in this case.
17 */
18 if (size & (size - 1)) {
19 BUG_ON(size > 0x80000000);
20 size = roundup_pow_of_two(size);
21 }
22
23 buffer = kmalloc(size, gfp_mask);
24 if (!buffer)
25 return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
26
27 ret = kfifo_init(buffer, size, gfp_mask, lock);
28
29 if (IS_ERR(ret))
30 kfree(buffer);
31
32 return ret;
33}
34EXPORT_SYMBOL(kfifo_alloc);
35静态声明kfifo
静态声明kfifo比较简单,但不太常用
例如下面会创建一个名称为name,大小为size的kfifo对象。和前面一样,size必须是2的幂
2
3
2INIT_KFIFO(name);
3
四、入队列(kfifo_put)
- 将数据推入队列使用这个函数
kfifo_put
参数:把buffer所指的len字节数据拷贝到fifo所指的队列中
返回值:成功返回推入的数据长度。如果队列中的空闲字节小于len,则该函数值最多可拷贝队列可用空间那么多的数据,这样的话,返回值可能小于len,甚至会返回0,这时意味着没有任何数据被推入
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
2 * kfifo_put - puts some data into the FIFO
3 * @fifo: the fifo to be used.
4 * @buffer: the data to be added.
5 * @len: the length of the data to be added.
6 *
7 * This function copies at most @len bytes from the @buffer into
8 * the FIFO depending on the free space, and returns the number of
9 * bytes copied.
10 */
11static inline unsigned int kfifo_put(struct kfifo *fifo,
12 unsigned char *buffer, unsigned int len)
13{
14 unsigned long flags;
15 unsigned int ret;
16
17 spin_lock_irqsave(fifo->lock, flags);
18
19 ret = __kfifo_put(fifo, buffer, len);
20
21 spin_unlock_irqrestore(fifo->lock, flags);
22
23 return ret;
24}
25
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
2 * __kfifo_put - puts some data into the FIFO, no locking version
3 * @fifo: the fifo to be used.
4 * @buffer: the data to be added.
5 * @len: the length of the data to be added.
6 *
7 * This function copies at most @len bytes from the @buffer into
8 * the FIFO depending on the free space, and returns the number of
9 * bytes copied.
10 *
11 * Note that with only one concurrent reader and one concurrent
12 * writer, you don't need extra locking to use these functions.
13 */
14unsigned int __kfifo_put(struct kfifo *fifo,
15 unsigned char *buffer, unsigned int len)
16{
17 unsigned int l;
18
19 len = min(len, fifo->size - fifo->in + fifo->out);
20
21 /*
22 * Ensure that we sample the fifo->out index -before- we
23 * start putting bytes into the kfifo.
24 */
25
26 smp_mb();
27
28 /* first put the data starting from fifo->in to buffer end */
29 l = min(len, fifo->size - (fifo->in & (fifo->size - 1)));
30 memcpy(fifo->buffer + (fifo->in & (fifo->size - 1)), buffer, l);
31
32 /* then put the rest (if any) at the beginning of the buffer */
33 memcpy(fifo->buffer, buffer + l, len - l);
34
35 /*
36 * Ensure that we add the bytes to the kfifo -before-
37 * we update the fifo->in index.
38 */
39
40 smp_wmb();
41
42 fifo->in += len;
43
44 return len;
45}
46EXPORT_SYMBOL(__kfifo_put);
47
五、出队列(kfifo_get)
- 将数据推出队列使用这个函数
kfifo_get
参数:从fifo所指的队列中拷贝出长度为len字节的数据到buffer所指的缓冲中
返回值:成功返回拷贝的数据长度。如果队列中数据大小小于len,则该函数拷贝出的数据必然小于需要的数据大小
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2 * kfifo_get - gets some data from the FIFO
3 * @fifo: the fifo to be used.
4 * @buffer: where the data must be copied.
5 * @len: the size of the destination buffer.
6 *
7 * This function copies at most @len bytes from the FIFO into the
8 * @buffer and returns the number of copied bytes.
9 */
10static inline unsigned int kfifo_get(struct kfifo *fifo,
11 unsigned char *buffer, unsigned int len)
12{
13 unsigned long flags;
14 unsigned int ret;
15
16 spin_lock_irqsave(fifo->lock, flags);
17
18 ret = __kfifo_get(fifo, buffer, len);
19
20 /*
21 * optimization: if the FIFO is empty, set the indices to 0
22 * so we don't wrap the next time
23 */
24 if (fifo->in == fifo->out)
25 fifo->in = fifo->out = 0;
26
27 spin_unlock_irqrestore(fifo->lock, flags);
28
29 return ret;
30}
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
2 * __kfifo_get - gets some data from the FIFO, no locking version
3 * @fifo: the fifo to be used.
4 * @buffer: where the data must be copied.
5 * @len: the size of the destination buffer.
6 *
7 * This function copies at most @len bytes from the FIFO into the
8 * @buffer and returns the number of copied bytes.
9 *
10 * Note that with only one concurrent reader and one concurrent
11 * writer, you don't need extra locking to use these functions.
12 */
13unsigned int __kfifo_get(struct kfifo *fifo,
14 unsigned char *buffer, unsigned int len)
15{
16 unsigned int l;
17
18 len = min(len, fifo->in - fifo->out);
19
20 /*
21 * Ensure that we sample the fifo->in index -before- we
22 * start removing bytes from the kfifo.
23 */
24
25 smp_rmb();
26
27 /* first get the data from fifo->out until the end of the buffer */
28 l = min(len, fifo->size - (fifo->out & (fifo->size - 1)));
29 memcpy(buffer, fifo->buffer + (fifo->out & (fifo->size - 1)), l);
30
31 /* then get the rest (if any) from the beginning of the buffer */
32 memcpy(buffer + l, fifo->buffer, len - l);
33
34 /*
35 * Ensure that we remove the bytes from the kfifo -before-
36 * we update the fifo->out index.
37 */
38
39 smp_mb();
40
41 fifo->out += len;
42
43 return len;
44}
45EXPORT_SYMBOL(__kfifo_get);
46
六、重置队列(kfifo_reset)
-
重置kfifo,排期所有队列的内容
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
2 * kfifo_reset - removes the entire FIFO contents
3 * @fifo: the fifo to be emptied.
4 */
5static inline void kfifo_reset(struct kfifo *fifo)
6{
7 unsigned long flags;
8
9 spin_lock_irqsave(fifo->lock, flags);
10
11 __kfifo_reset(fifo);
12
13 spin_unlock_irqrestore(fifo->lock, flags);
14}
15
16/**
17 * __kfifo_reset - removes the entire FIFO contents, no locking version
18 * @fifo: the fifo to be emptied.
19 */
20static inline void __kfifo_reset(struct kfifo *fifo)
21{
22 fifo->in = fifo->out = 0;
23}
24
七、撤销队列(kfifo_free)
-
撤销一个使用kfifo_alloc()分配的队列,可以调研kfifo_free
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2 * kfifo_free - frees the FIFO
3 * @fifo: the fifo to be freed.
4 */
5void kfifo_free(struct kfifo *fifo)
6{
7 kfree(fifo->buffer);
8 kfree(fifo);
9}
10EXPORT_SYMBOL(kfifo_free);
11
- 如果你是使用kfifo_init()方法创建的队列,那么需要负责相关的缓冲。具体方法取决于你是如何创建它的
