一、strings和strconv的使用
-
- strings.HasPrefix(s string, prefix string) bool:判断字符串s是否以prefix开头 。
-
- strings.HasSuffix(s string, suffix string) bool:判断字符串s是否以suffix结尾。
-
- strings.Index(s string, str string) int:判断str在s中首次出现的位置,如果没有出现,则返回-1
-
- strings.LastIndex(s string, str string) int:判断str在s中最后出现的位置,如果没有出现,则返回-1
-
- strings.Replace(str string, old string, new string, n int):字符串替换
-
- strings.Count(str string, substr string)int:字符串计数
-
- strings.Repeat(str string, count int)string:重复count次str
-
- strings.ToLower(str string)string:转为小写
-
- strings.ToUpper(str string)string:转为大写
-
- strings.TrimSpace(str string):去掉字符串首尾空白字符
-
- strings.Trim(str string, cut string):去掉字符串首尾cut字符
-
- strings.TrimLeft(str string, cut string):去掉字符串首cut字符
-
- strings.TrimRight(str string, cut string):去掉字符串首cut字符
-
- strings.Field(str string):返回str空格分隔的所有子串的slice
-
- strings.Split(str string, split string):返回str split分隔的所有子串的slice
-
- strings.Join(s1 []string, sep string):用sep把s1中的所有元素链接起来
-
- strings.Itoa(i int):把一个整数i转成字符串
-
- strings.Atoi(str string)(int, error):把一个字符串转成整数
练习1:判断一个url是否以http://开头,如果不是,则加上http://,判断一个路径是否以“/”结尾,如果不是,则加上/。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
2
3import (
4 "fmt"
5 "strings"
6)
7
8func urlProcess(url string) string {
9 result := strings.HasPrefix(url, "http://")
10 if !result {
11 url = fmt.Sprintf("http://%s", url)
12 }
13 return url
14}
15func pathProcess(path string) string {
16 result := strings.HasSuffix(path, "/")
17 if !result {
18 path = fmt.Sprintf("%s/", path)
19 }
20 strings.Replace()
21 return path
22
23}
24
25func main() {
26 var (
27 url string
28 path string
29 )
30
31 fmt.Printf("请输入一个url地址和path路径:")
32 fmt.Scanf("%s%s", &url, &path)
33
34 url = urlProcess(url)
35 path = pathProcess(path)
36
37 fmt.Println(url)
38 fmt.Println(path)
39}
40
41// 请输入一个url地址和path路径: www.baidu.com c:/python
42
练习一
练习2:写一个函数分别演示Replace、Count、Repeat、ToLower、ToUpper等的用法


2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
2
3import (
4 "fmt"
5 "strconv"
6 "strings"
7)
8
9func main() {
10 str := " hello world abc \n"
11 result := strings.Replace(str, "world", "you", 1)
12 fmt.Println("replace:", result)
13
14 count := strings.Count(str, "l")
15 fmt.Println("count:", count)
16
17 result = strings.Repeat(str, 3)
18 fmt.Println("repeat:", result)
19
20 result = strings.ToLower(str)
21 fmt.Println("tolower:", result)
22
23 result = strings.ToUpper(str)
24 fmt.Println("toupper:", result)
25
26 result = strings.TrimSpace(str)
27 fmt.Println("trimspace:", result)
28
29 result = strings.Trim(str, " \n\r")
30 fmt.Println("trim", result)
31
32 result = strings.TrimLeft(str, " \n\r")
33 fmt.Println("trimleft:", result)
34
35 result = strings.TrimRight(str, " \n\r")
36 fmt.Println("trimright:", result)
37
38 split_result := strings.Fields(str)
39 for i := 0; i < len(split_result); i++ {
40 fmt.Println(split_result[i])
41 }
42
43 split_result = strings.Split(str, "l")
44 for i := 0; i < len(split_result); i++ {
45 fmt.Println(split_result[i])
46 }
47
48 str2 := strings.Join(split_result, "l")
49 fmt.Println("join:", str2)
50
51 str2 = strconv.Itoa(1000)
52 fmt.Println("Itoa:", str2)
53
54 num, err := strconv.Atoi(str2)
55 if err != nil {
56 fmt.Println("can not convert str to int", err)
57 }
58 fmt.Println("number is:", num)
59}
60
练习二
二、时间和日期类型
-
- time包
-
- time.Time类型,用来表示时间
-
- 获取当前时间,now := time.Now()
-
- time.Now().Day(),time.Now().Minute(),time.Now().Month(),time.Now().Year()
-
- 格式化,fmt.Printf(“%02d/%02d%02d %02d:%02d:%02d”, now.Year()…)
-
- time.Duration用来表示纳秒
-
-
一些常量:
-
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2Nanosecond Duration = 1
3Microsecond = 1000 * Nanosecond
4Millisecond = 1000 * Microsecond
5Second = 1000 * Millisecond
6Minute = 60 * Second
7Hour = 60 * Minute
8)
9
-
-
格式化:
-
2
3
4
5
2fmt.Println(now.Format(“02/1/2006 15:04”))
3fmt.Println(now.Format(“2006/1/02 15:04”))
4fmt.Println(now.Format(“2006/1/02"))
5
练习:写一个程序,获取当前时间,并格式化成 2017/06/15 08:05:00形式, 统计一段代码的执行耗时,单位精确到微秒。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2
3import (
4 "fmt"
5 "time"
6)
7
8func test() {
9 time.Sleep(time.Millisecond * 100)
10}
11
12func main() {
13 now := time.Now()
14 fmt.Println(now.Format("2006/01/02 15:04:05"))
15 start := time.Now().UnixNano() // 1970年到现在的纳秒数
16 test()
17 end := time.Now().UnixNano()
18
19 fmt.Println("cost:%d us\n", (end-start)/1000)
20}
21
三、指针类型
-
- 普通类型,变量存的就是值,也叫值类型
-
- 获取变量的地址,用&,比如: var a int, 获取a的地址:&a
-
- 指针类型,变量存的是一个地址,这个地址存的才是值
-
- 获取指针类型所指向的值,使用:*,比如:var *p int, 使用*p获取p指向的值
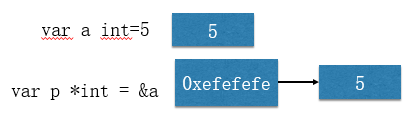
练习:写一个程序,获取一个变量的地址,并打印到终端,写一个函数,传入一个int类型的指针,并在函数中修改所指向的值。在main函数中调用这个函数,并把修改前后的值打印到终端,观察结果
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
2
3import "fmt"
4
5func modify(n *int) {
6 fmt.Println(n)
7 *n = 10000000
8 return
9}
10
11func main() {
12 var a int = 10 // 整数类型
13 fmt.Println(&a) // 取地址
14 fmt.Println(a) // 取变量值
15
16 var p *int // 指针类型
17 p = &a
18 fmt.Println(p) // 取地址
19 fmt.Println(*p) // 取指针指向的变量值
20 *p = 100 // 修改指针地址指向的变量值
21 fmt.Println(a) // 响应的a的变量值也更改
22
23 var b int = 999
24 p = &b
25 *p = 5
26
27 fmt.Println(a)
28 fmt.Println(b)
29
30 modify(&a)
31 fmt.Println(a)
32}
33
四、流程控制
1. if / else 分支判断
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
2if condition1 {
3}
4
5方式二:
6if condition1 {
7
8} else {
9
10方式三:
11}
12if condition1 {
13
14} else if condition2 {
15
16} else if condition3 {
17} else {
18}
19
20方式四:
21if condition1 {
22
23}
24else {
25
26}
27
例子
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2import “fmt”
3func main() {
4 bool1 := true
5 if bool1 {
6 fmt.Printf(“The value is true\n”)
7 } else {
8 fmt.Printf(“The value is false\n”)
9 }
10}
11
练习:写一个程序,从终端读取输入,并转成整数,如果转成整数出错,则输出 “can not convert to int”,并返回。否则输出该整数。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2
3import (
4 "fmt"
5 "strconv"
6)
7
8func main() {
9 var str string
10 fmt.Printf("请输入一个字符串:")
11 fmt.Scanf("%s", &str)
12
13 number, err := strconv.Atoi(str)
14 if err != nil {
15 fmt.Println("convert failed, err:", err)
16 return
17 }
18 fmt.Println(number)
19}
20
2. switch case语句
语法
2
3
4
5
6
7
2 case var1:
3 case var2:
4 case var3:
5 default:
6 }
7
写法
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
2 var i = 0
3 switch i {
4 case 0:
5 case 1:
6 fmt.Println(“1”)
7 case 2:
8 fmt.Println(“2”)
9 default:
10 fmt.Println(“def”)
11 }
12
13写法二
14 var i = 0
15 switch i {
16 case 0:
17 fallthrough
18 case 1:
19 fmt.Println(“1”)
20 case 2:
21 fmt.Println(“2”)
22 default:
23 fmt.Println(“def”)
24 }
25
26写法三
27 var i = 0
28 switch i {
29 case 0, 1:
30 fmt.Println(“1”)
31 case 2:
32 fmt.Println(“2”)
33 default:
34 fmt.Println(“def”)
35 }
36写法四
37 var i = 0
38 switch {
39 condition1:
40 fmt.Println(“i > 0 and i < 10”)
41 condition2:
42 fmt.Println(“i > 10 and i < 20”)
43 default:
44 fmt.Println(“def”)
45 }
46
47 var i = 0
48 switch {
49 case i > 0 && i < 10:
50 fmt.Println(“i > 0 and i < 10”)
51 case i > 10 && i < 20:
52 fmt.Println(“i > 10 and i < 20”)
53 default:
54 fmt.Println(“def”)
55 }
56写法五
57 switch i := 0 {
58 case i > 0 && i < 10:
59 fmt.Println(“i > 0 and i < 10”)
60 case i > 10 && i < 20:
61 fmt.Println(“i > 10 and i < 20”)
62 default:
63 fmt.Println(“def”)
64 }
65
练习:猜数字,写一个程序,随机生成一个0到100的整数n,然后用户在终端,输入数字,如果和n相等,则提示用户猜对了。如果不相等,则提示用户,大于或小于n。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3import (
4 "fmt"
5 "math/rand"
6)
7
8func main() {
9 var n int
10 n = rand.Intn(100)
11 fmt.Println(n)
12 for {
13 var input int
14 fmt.Printf("请输入一个0-100的整数:")
15 fmt.Scanf("%d\n", &input)
16 flag := false
17 switch {
18 case input == n:
19 flag = true
20 fmt.Println("you are right")
21 case input < n:
22 fmt.Printf("%d is smaller\n", input)
23 case input > n:
24 fmt.Printf("%d is bigger\n", input)
25 }
26 if flag {
27 break
28 }
29 }
30}
31
3. for 语句
写法1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2}
3
4for i := 0 ; i < 100; i++ {
5fmt.Printf(“i=%d\n”, i)
6}
7
练习:写一个程序,在终端打印如下图形
A
AA
AAA
AAAA
AAAAA
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
2
3import "fmt"
4
5func Print(n int) {
6 for i := 1; i <= n; i++ {
7 for j := 0; j < i; j++ {
8 fmt.Printf("A")
9 }
10 fmt.Println()
11 }
12}
13
14func main() {
15 Print(6)
16}
17
写法二
2
3
2}
3
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2 fmt.Println(“i > 0”)
3}
4
5for true {
6 fmt.Println(“i > 0”)
7}
8
9for {
10 fmt.Println(“i > 0”)
11}
12
写法三 for range语句
2
3
4
5
2for i, v := range str {
3 fmt.Printf(“index[%d] val[%c] len[%d]\n”, i, v, len([]byte(v)))
4}
5
用来遍历数组、slice、map、chan
写法四 break,coutinue语句
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2for i, v := range str {
3 if i > 2 {
4 continue
5 }
6 if (i > 3) {
7 break }
8 fmt.Printf(“index[%d] val[%c] len[%d]\n”, i, v, len([]byte(v)))
9}
10
4. goto和label语句
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
2import "fmt"
3func main() {
4LABEL1:
5 for i := 0; i <= 5; i++ {
6 for j := 0; j <= 5; j++ {
7 if j == 4 {
8 continue LABEL1
9 }
10 fmt.Printf("i is: %d, and j is: %d\n", i, j)
11 }
12 }
13}
14
15
16package main
17
18func main() {
19 i := 0
20HERE:
21 print(i)
22 i++
23 if i == 5 {
24 return
25 }
26 goto HERE
27}
28
五、函数
1. 语法
2
2

2. golang 函数特点
-
a. 不支持重载,一个包不能有两个名字一样的函数
-
b. 函数是一等公民,函数也是一种类型,一个函数可以赋值给变量
-
c. 匿名函数
-
d. 多返回值
例
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2
3import "fmt"
4
5func add(a, b int) int {
6 return a + b
7}
8
9func test() {
10 return
11}
12
13func main() {
14 c := add
15 sum := c(200, 300)
16 fmt.Println(sum)
17
18 str := "hello world,中国"
19 for index, val := range str {
20 fmt.Printf("index[%d] val[%c] len[%d]\n", index, val, len([]byte(string(val))))
21 }
22}
23
例2
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
2
3import "fmt"
4
5type op_func func(int, int) int
6
7func add(a, b int) int {
8 return a + b
9}
10
11func sub(a, b int) int {
12 return a - b
13}
14
15func operator(op func(int, int) int, a, b int) int {
16 return op(a, b)
17}
18
19func main() {
20 var c op_func
21 c = add
22 // c := add
23
24 sum := operator(c, 100, 200)
25 dif := operator(sub, 100, 200)
26
27 fmt.Println(sum)
28 fmt.Println(dif)
29}
30
3. 函数传参的两种方式
1). 值传递
2) 引用传递
注意1:无论是值传递,还是引用传递,传递给函数的都是变量的副本,不过,值传递是值的拷贝。引用传递是地址的拷贝,一般来说,地址拷贝更为高效。而值拷贝取决于拷贝的对象大小,对象越大,则性能越低。
注意2:map、slice、chan、指针、interface默认以引用的方式传递
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3import "fmt"
4
5func modify(a int) {
6 a = 100
7}
8
9func main() {
10 a := 8
11 fmt.Println(a)
12 modify(a)
13 fmt.Println(a)
14}
15
4. 命名返回值的名字
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2 c = a + b
3 return
4}
5
6func calc(a, b int) (sum int, avg int) {
7 sum = a + b
8 avg = (a +b)/2
9 return
10}
11
5. _标识符,用来忽略返回值
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2 sum = a + b
3 avg = (a +b)/2
4 return}
5func main() {
6 sum, _ := calc(100, 200)
7}
8
6. 可变参数

注意:其中arg是一个slice,我们可以通过arg[index]依次访问所有参数,通过len(arg)来判断传递参数的个数
练习:写一个函数add,支持1个或多个int相加,并返回相加结果, 写一个函数concat,支持1个或多个string相拼接,并返回结果
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
2
3import "fmt"
4
5func add(a int, arg ...int) int {
6 var sum int = a
7 for i := 0; i < len(arg); i++ {
8 sum += arg[i]
9 }
10 return sum
11}
12
13func concat(a string, arg ...string) (result string) {
14 result = a
15 for i := 0; i < len(arg); i++ {
16 result += arg[i]
17 }
18 return
19}
20
21func main() {
22 sum := add(10, 3, 5, 6, 6)
23 fmt.Println(sum)
24
25 res := concat("hello", " ", "world")
26 fmt.Println(res)
27}
28
7. defer用途
- 1). 当函数返回时,执行defer语句。因此,可以用来做资源清理
- 2). 多个defer语句,按先进后出的方式执行
- 3). defer语句中的变量,在defer声明时就决定了。
关闭文件句柄
2
3
4
5
6
7
2file := open(filename)
3defer file.Close()
4
5//文件操作
6}
7
锁资源释放
2
3
4
5
6
2mc.Lock()
3defer mc.Unlock()
4//其他操作
5}
6
数据库连接释放
2
3
4
5
6
2conn := openDatabase()
3defer conn.Close()
4//其他操作
5}
6
defer示例


2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
2
3import "fmt"
4
5var (
6 result = func(a1 int, b1 int) int {
7 return a1 + b1
8 }
9)
10
11func test(a, b int) int {
12 result := func(a1 int, b1 int) int {
13 return a1 + b1
14 }(a, b)
15 return result
16}
17
18func main() {
19 fmt.Println(test(100, 200))
20 fmt.Println(result(100, 200))
21
22 var i int = 0
23 // defer语句编译的时候会把语句放入栈中,函数结尾的时候一个一个出栈执行
24 defer fmt.Println(i)
25 defer fmt.Println("second")
26
27 i = 10
28 fmt.Println(i)
29}
30
defer示例
本节作业
-
- 编写程序,在终端输出九九乘法表。
-
- 一个数如果恰好等于它的因子之和,这个数就称为“完数”。例如6=1+2+3.编程找出1000以内的所有完数。
-
- 输入一个字符串,判断其是否为回文。回文字符串是指从左到右读和从右到左读完全相同的字符串。
-
- 输入一行字符,分别统计出其中英文字母、空格、数字和其它字符的个数。
-
- 计算两个大数相加的和,这两个大数会超过int64的表示范围.
参考


2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
2
3import "fmt"
4
5func multi() {
6 for i := 1; i < 10; i++ {
7 for j := 1; j <= i; j++ {
8 fmt.Printf("%d*%d=%d\t", i, j, i*j)
9 }
10 fmt.Println()
11 }
12}
13
14func main() {
15 multi()
16}
17
作业一


2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
2
3import "fmt"
4
5func perfect(n int) bool {
6 var sum int = 0
7 for i := 1; i < n; i++ {
8 if n%i == 0 {
9 sum += i
10 }
11 }
12 return sum == n
13}
14
15func process(n int) {
16 var flag bool = false
17 for i := 1; i < n+1; i++ {
18 if perfect(i) {
19 flag = true
20 fmt.Println(i, "是完数")
21 }
22 }
23 if flag == false {
24 fmt.Println(n, "以内没有完数")
25 }
26}
27
28func main() {
29 var n int
30 fmt.Printf("请输入一个数字:")
31 fmt.Scanf("%d", &n)
32 process(n)
33}
34
作业二


2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
2
3import "fmt"
4
5func process(str string) bool {
6 // rune代表一个字符(中文英文都可以)
7 // byte代表一个字节,一个中文字符代表三个字节
8 t := []rune(str)
9 length := len(t)
10 for i, _ := range t {
11 if i == length/2 {
12 break
13 }
14 last := length - i - 1
15 if t[i] != t[last] {
16 return false
17 }
18 }
19 return true
20}
21
22func main() {
23 var str string
24 fmt.Printf("请输入一个字符串:")
25 fmt.Scanf("%s", &str)
26 if process(str) {
27 fmt.Println(str, "是回文: yes")
28 } else {
29 fmt.Println(str, "是回文: no")
30 }
31}
32
作业三


2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
2
3import (
4 "bufio"
5 "fmt"
6 "os"
7)
8
9func process(str string) (word_count int, sapce_counr int, number_count int, other_count int) {
10 t := []rune(str)
11 for _, v := range t {
12 switch {
13 case v >= 'a' && v <= 'z':
14 fallthrough
15 case v >= 'A' && v <= 'Z':
16 word_count++
17 case v == ' ':
18 sapce_counr++
19 case v >= '0' && v <= '9':
20 number_count++
21 default:
22 other_count++
23 }
24 }
25 return
26}
27
28func main() {
29 fmt.Printf("请输入一个字符串:")
30 reader := bufio.NewReader(os.Stdin)
31 result, _, err := reader.ReadLine()
32 if err != nil {
33 fmt.Println("read from console err", err)
34 return
35 }
36 wc, sc, nc, oc := process(string(result))
37 fmt.Printf("word_count:%d\nspace_count:%d\nnumber_count:%d\nother_count:%d", wc, sc, nc, oc)
38
39}
40
作业四


2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
2
3import (
4 "bufio"
5 "fmt"
6 "os"
7 "strings"
8)
9
10func multi(str1, str2 string) (result string) {
11 if len(str1) == 0 && len(str2) == 0 {
12 result = "0"
13 return
14 }
15
16 var index1 = len(str1) - 1
17 var index2 = len(str2) - 1
18 var left int
19
20 for index1 >= 0 && index2 >= 0 {
21 c1 := str1[index1] - '0'
22 c2 := str2[index2] - '0'
23
24 sum := int(c1) + int(c2) + left
25 if sum >= 10 {
26 left = 1
27 } else {
28 left = 0
29 }
30 c3 := (sum % 10) + '0'
31 result = fmt.Sprintf("%c%s", c3, result)
32 index1--
33 index2--
34 }
35 for index1 >= 0 {
36 c1 := str1[index1] - '0'
37 sum := int(c1) + left
38 if sum >= 10 {
39 left = 1
40 } else {
41 left = 0
42 }
43 c3 := (sum % 10) + '0'
44 result = fmt.Sprintf("%c%s", c3, result)
45 index1--
46 }
47 for index2 >= 0 {
48 c1 := str2[index2] - '0'
49 sum := int(c1) + left
50 if sum >= 10 {
51 left = 1
52 } else {
53 left = 0
54 }
55 c3 := (sum % 10) + '0'
56 result = fmt.Sprintf("%c%s", c3, result)
57 index2--
58 }
59 if left == 1 {
60 result = fmt.Sprintf("1%s", result)
61 }
62 return
63}
64
65func main() {
66 fmt.Printf("请输入一个字符串:")
67 reader := bufio.NewReader(os.Stdin)
68 result, _, err := reader.ReadLine()
69 if err != nil {
70 fmt.Println("read from console err", err)
71 return
72 }
73 strSlice := strings.Split(string(result), "+")
74 if len(strSlice) != 2 {
75 fmt.Println("please input a+b")
76 return
77 }
78 strNumber1 := strings.TrimSpace(strSlice[0])
79 strNumber2 := strings.TrimSpace(strSlice[1])
80 fmt.Println(multi(strNumber1, strNumber2))
81}
82
作业五
