目录
-
编辑和运行shell脚本
-
编辑
- 运行
-
shell变量
-
命名规则
- 建改删用
-
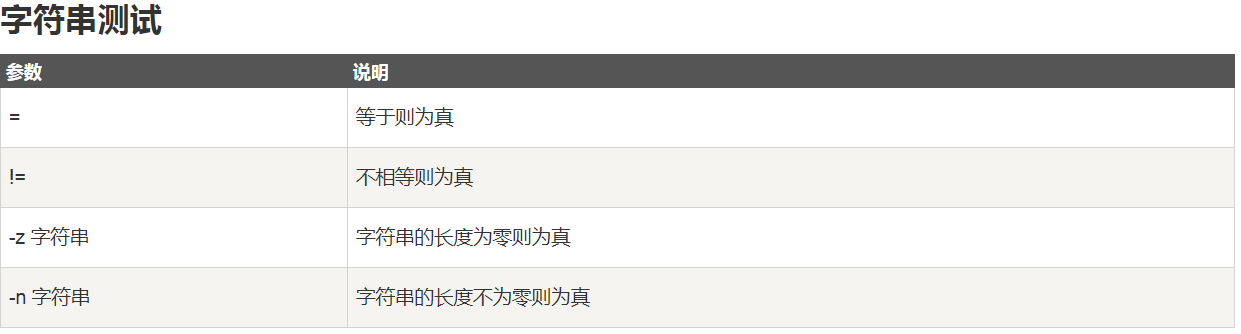
shell字符串
-
shell数组
-
shell注释
-
传递参数
-
运算
-
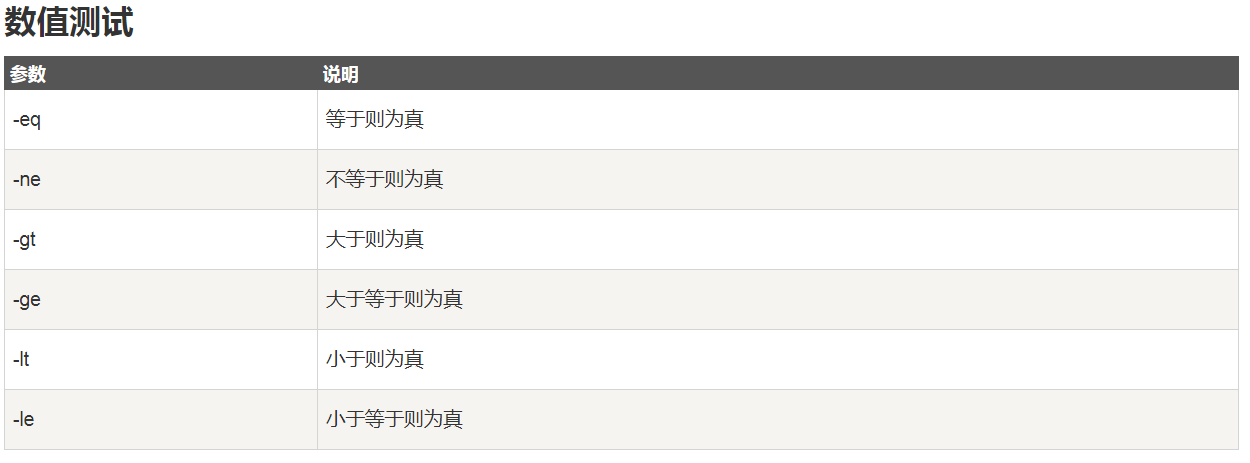
算术运算
- 关系运算
- 布尔运算和逻辑运算
- 字符串运算
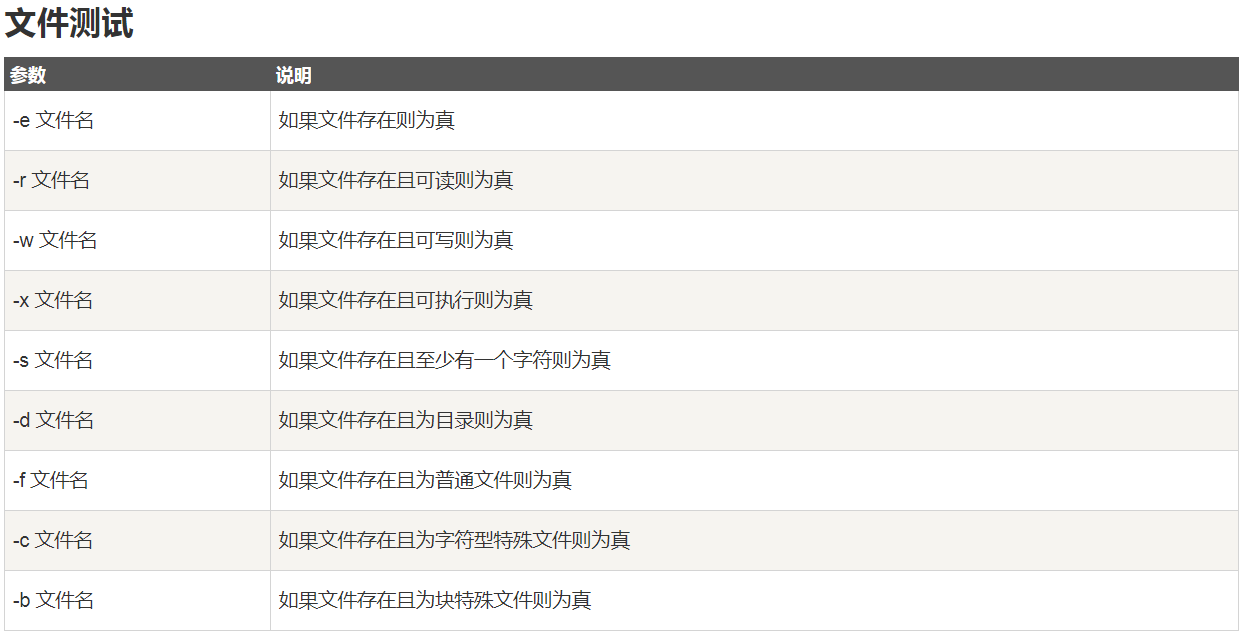
- 文件测试运算符
-
打印命令
-
echo命令
- printf命令
-
shell函数
-
函数定义
- 参数和返回值
-
test命令
-
输入输出重定向
-
重定向标准输入,标准输出
- 重定向标准输出和标准错误到一个位置
- 交互式(多行)输入
- 不要显示输出
-
导入其他文件
-
流程控制
-
条件分支
- 循环
参考菜鸟教程,把shell编程总结下。
编辑和运行shell脚本
编辑
编辑器:vim pycharm vscode等等能够编写代码的文本编辑器
运行
解释器:Linux 的 Shell 种类众多,常见的有:
- Bourne Shell(/usr/bin/sh或/bin/sh)
- Bourne Again Shell(/bin/bash)
- C Shell(/usr/bin/csh)
- K Shell(/usr/bin/ksh)
- Shell for Root(/sbin/sh)
运行方式一般有两种:
-
在代码开头加上默认的解释器,如
2
3
2
3
然后将shell脚本文件改为可执行文件
2
3
2
3
就可以直接用
2
3
2
3
运行了。
shell变量
命名规则
-
只由(大写、小写)英文字母,数字,下划线组成
-
不能用数字开头
-
不能使用bash保留的关键字,可使用
2
3
2
3
查看所有关键字。
建改删用
-
创建一个没有的shell变量
2
3
2
3
- 改变一个已有的shell变量
(1)改变量的值
2
3
4
2my_var="bad" #改为“bad”了
3
4
(2)改权限
2
3
4
2readonly my_var #改为只读,这样就不能被修改,也不能被删除
3
4
-
删除一个已有的变量
2
3
4
2unset my_var
3
4
-
使用变量的值
2
3
4
2echo this is a ${my_var} day. #加上花括号,限定变量名的界限,以免引起混乱
3
4
shell字符串
-
单引号中的所有字符都保持原样,不涉及转义或取变量的值
-
双引号中涉及转义和取变量的值
-
也可以不用引号
-
拼接字符串:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2# 使用双引号拼接
3greeting="hello, "$your_name" !"
4greeting_1="hello, ${your_name} !"
5echo $greeting $greeting_1
6# 使用单引号拼接
7greeting_2='hello, '$your_name' !'
8greeting_3='hello, ${your_name} !'
9echo $greeting_2 $greeting_3
10
11
输出为:
hello, runoob ! hello, runoob !
hello, runoob ! hello, ${your_name} !
注意第三个使用单引号的拼接方式
-
获取字符串长度
2
3
4
2echo ${#your_name} # 6
3
4
-
字符串切片
2
3
4
5
2echo ${string:1:4} # 输出unoo,即从编号1开始的4个字符,注意shell的字符串从0开始编号,这一点和python一致
3echo ${string:2} # 输出noob is a great site,即从编号2开始的所有字符
4
5
-
字符串查找
2
3
4
2echo `expr index "${string}" io` # 输出4,即i或者o最开始出现的地方,注意这时候index从1开始计算,而不是0
3
4
shell数组
- 定义方法
(1) 使用空格作为分隔符
2
3
4
2echo ${array_name[0]} # 输出value0
3
4
(2)使用换行作为分隔符
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2value0
3value1
4value2
5value3
6)
7
8
(3) 直接对下标进行赋值,注意shell数组的编号可以不连续,有什么就用什么,没有的下标也可以取值,但是是空的
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2array_name[1]=value1
3array_name[5]=value5
4echo ${array_name[@]}
5echo try 2
6echo ${array_name[2]}
7echo try 5
8echo ${array_name[5]}
9
10
输出为:
value0 value1 value5
try 2
try 5
value5
-
长度
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2array_name[1]=value1
3array_name[5]=value5
4# 取得数组元素的个数
5length=${#array_name[@]}
6echo first length: ${length}
7# 或者
8length=${#array_name[*]}
9echo second length: ${length}
10# 取得数组单个元素的长度
11length5=${#array_name[5]}
12echo one string length: ${length5}
13
14
输出为:
first length: 3
second length: 3
one string length: 6
shell注释
-
单行注释,使用#开头
-
多行注释
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
2echo here is a comment
3EOF
4
5echo it is not a comment
6
7
8:<<! # 使用!
9# 或者
10length=${#array_name[*]}
11echo second length: ${length}
12# 取得数组单个元素的长度
13length5=${#array_name[5]}
14echo one string length: ${length5}
15!
16
17
传递参数
- $0表示文件名,$1表示第一个命令行参数,$2表示第二个命令行参数。。。
- $#表示传到脚本的命令行参数个数
- "$*"以一个单字符串显示所有向脚本传递的参数
- "$@"以字符串数组显示所有向脚本传递的参数
运算
算术运算
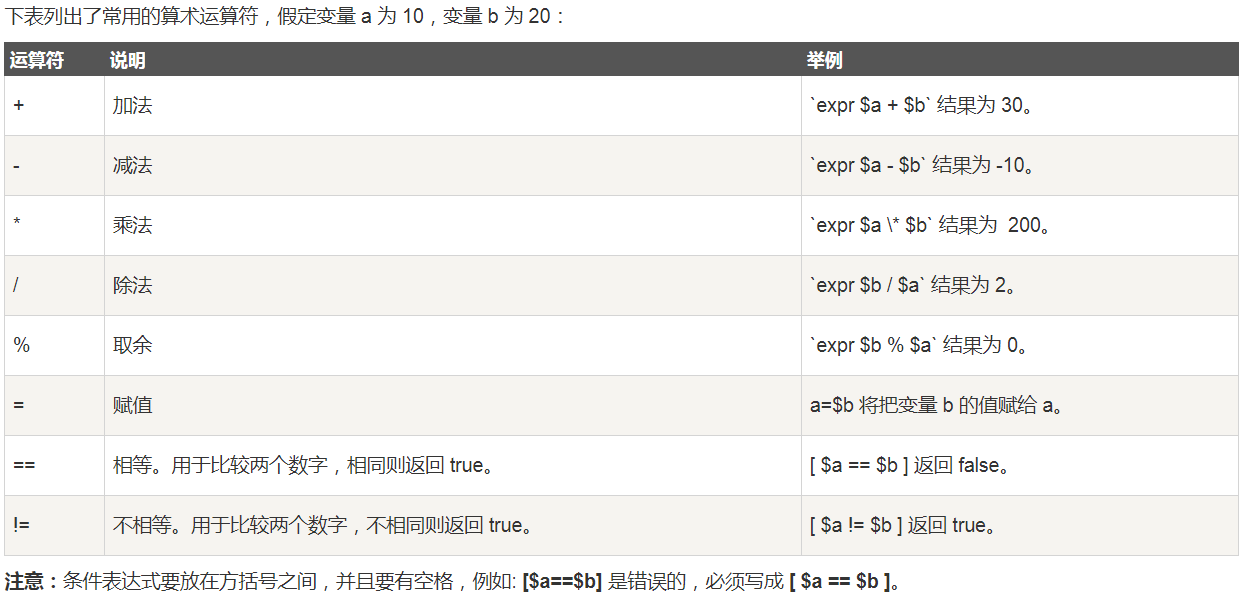
注意: 算术运算可以如下写
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3a=5
4b=6
5
6result=$[a+b] # 注意等号两边不能有空格
7echo "result 为: $result" # 11
8
9
关系运算
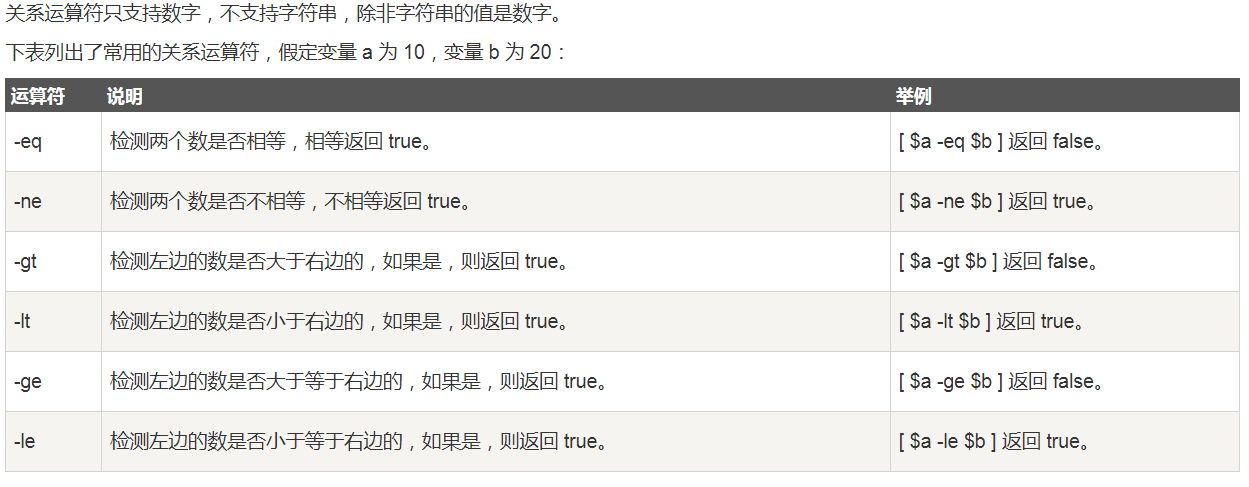
布尔运算和逻辑运算
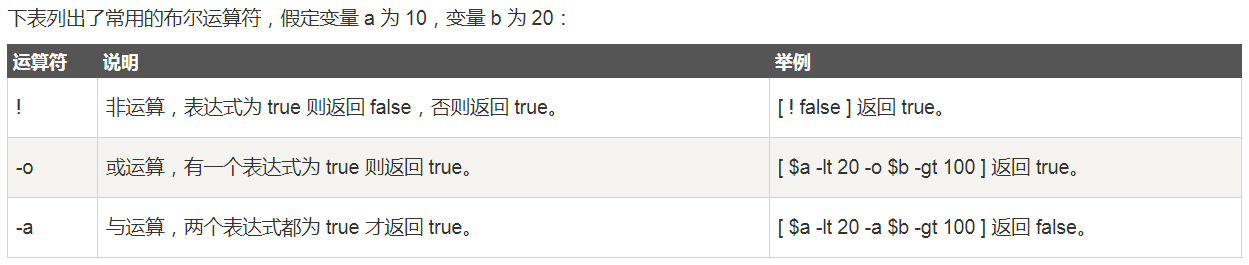

字符串运算

注意:>、<、==、!= 也可以进行字符串比较,只不过这个时候需要使用[[ ]]来进行条件判断,而且里面的逻辑运算要用&&和||,另外逻辑非!此时也可用
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3a="heri"
4b="here"
5if [[ $a < $b ]]
6then
7 echo 'a<b'
8else
9 echo 'a>=b'
10fi
11
12if [[ $a == $b ]]
13then
14 echo 'a=b'
15else
16 echo 'a!=b'
17fi
18
19
文件测试运算符
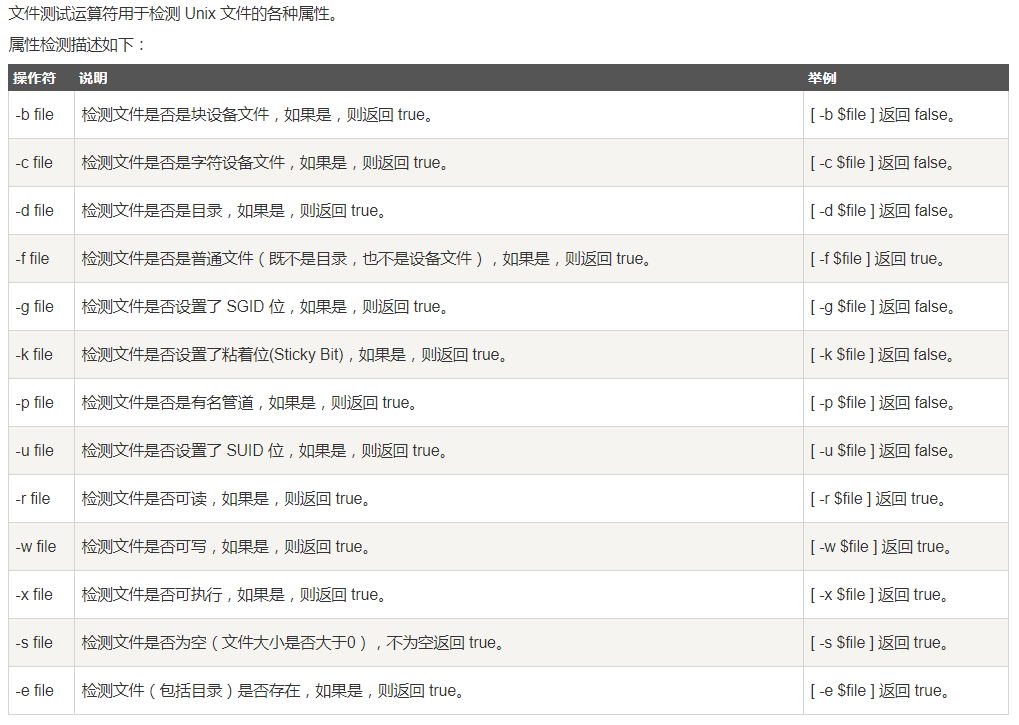
2
3
4
5
6
7
2if [ ! -d "TCGA/breast" ]
3then
4 mkdir "TCGA/breast"
5fi
6
7
打印命令
echo命令
输出字符串,自动添加换行符
-
单引号不转义
2
3
4
5
6
7
2echo 'yes.'
3#result:
4#ok, this is \"cp\".\n
5#yes.
6
7
-
双引号转义",但是不转义\n
2
3
4
5
6
2echo "yes."
3#ok, this is "cp".\n
4#yes.
5
6
-
-e 强制转义
2
3
4
5
6
7
2echo "yes."
3#ok, this is "cp".
4#
5#yes.
6
7
printf命令
输出字符串,不自动添加换行,但是格式化能力强
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
2# author:菜鸟教程
3# url:www.runoob.com
4
5# format-string为双引号
6printf "%d %s\n" 1 "abc"
7
8# 单引号与双引号效果一样
9printf '%d %s\n' 1 "abc"
10
11# 没有引号也可以输出
12printf %s abcdef
13
14# 格式只指定了一个参数,但多出的参数仍然会按照该格式输出,format-string 被重用
15printf %s abc def
16
17printf "%s\n" abc def
18
19printf "%s %s %s\n" a b c d e f g h i j
20
21# 如果没有 arguments,那么 %s 用NULL代替,%d 用 0 代替
22printf "%s and %d \n"
23#result:
24#1 abc
25#1 abc
26#abcdefabcdefabc
27#def
28#a b c
29#d e f
30#g h i
31#j
32# and 0
33
34
shell函数
函数定义
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
2demoFun(){
3 echo "这是我的第一个 shell 函数!"
4}
5
6#2:
7funWithReturn(){
8 echo "这个函数会对输入的两个数字进行相加运算..."
9 echo "输入第一个数字: "
10 read aNum
11 echo "输入第二个数字: "
12 read anotherNum
13 echo "两个数字分别为 $aNum 和 $anotherNum !"
14 return $(($aNum+$anotherNum)) # 带return
15}
16
17
参数和返回值
-
函数返回值在调用该函数后通过 $? 来获得,需要立即保存,否则就不能再看到了。当有return时,return的必须是0-255的整数,$?获得return的整数;当没有return时,$?获得函数最后一条命令运行成功与否的值,成功为0,不成功为1.
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2function demoFun1(){
3 echo "这是我的第一个 shell 函数!"
4 return `expr 1 + 1`
5}
6
7demoFun1
8echo $?
9
10function demoFun2(){
11 echo "这是我的第二个 shell 函数!"
12 expr 1 + 1
13}
14
15demoFun2
16echo $?
17demoFun1
18echo 在这里插入命令!
19echo $?
20
21# 结果:
22# 这是我的第一个 shell 函数!
23# 2
24# 这是我的第二个 shell 函数!
25# 2
26# 0
27# 这是我的第一个 shell 函数!
28# 在这里插入命令!
29# 0
30
31
- 函数参数用${n}获取
- 函数参数数目用$#获取
test命令
检查条件是否满足
-
数值
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2num2=100
3if test $[num1] -eq $[num2]
4then
5 echo '两个数相等!'
6else
7 echo '两个数不相等!'
8fi
9
10
-
字符串
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2num2="runoob"
3if test $num1 = $num2
4then
5 echo '两个字符串相等!'
6else
7 echo '两个字符串不相等!'
8fi
9
10
-
文件
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2if test -e ./bash
3then
4 echo '文件已存在!'
5else
6 echo '文件不存在!'
7
8fi
9
10
- 多重条件
Shell还提供了与( -a )、或( -o )、非( ! )三个逻辑操作符用于将测试条件连接起来,其优先级为:"!“最高,”-a"次之,"-o"最低。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2if test -e ./notFile -o -e ./bash
3then
4 echo '至少有一个文件存在!'
5else
6 echo '两个文件都不存在'
7fi
8
9
输入输出重定向
标准输入(stdin)的文件描述符为0,标准输出(stdout)的文件描述符为1,标准错误(stderr)的文件描述符为2。通过重定向,可以从文件读数据,并且输出到文件。
重定向标准输入,标准输出
-
改写方式
2
3
2
3
-
追加方式
2
3
2
3
重定向标准输出和标准错误到一个位置
2
3
2
3
交互式(多行)输入
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2 欢迎来到
3 菜鸟教程
4 www.runoob.com
5EOF
63 # 返回命令结果
7
8
或者
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3wc -l << EOF
4 欢迎来到
5 菜鸟教程
6 www.runoob.com
7EOF
8
9
不要显示输出
当不想要显示输出时,重定向到/dev/null
2
3
2
3
导入其他文件
封装公用部分为file,在其他文件中使用时,只需要导入这个shell文件就行了。有两种写法
2
3
4
5
2#或者
3source file
4
5
第一个shell文件为
2
3
4
5
6
7
2# author:菜鸟教程
3# url:www.runoob.com
4
5url="http://www.runoob.com"
6
7
第二个shell文件为
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
2# author:菜鸟教程
3# url:www.runoob.com
4
5#使用 . 号来引用test1.sh 文件
6. ./test1.sh
7
8# 或者使用以下包含文件代码
9# source ./test1.sh
10
11echo "菜鸟教程官网地址:${url}"
12
13
流程控制
条件分支
- if else模式
有else或者没有else都行
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2# 或者脚本写法,把;用换行替换,一些关键字后的空格用换行缩进替换
3if [ $(ps -ef | grep -c "ssh") -gt 1 ]
4then
5 echo "true"
6fi
7
8
- if else-if else模式
想象一个二叉树,不断进行条件判断进行延伸
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2b=20
3if [ $a == $b ]
4then
5 echo "a 等于 b"
6elif [ $a -gt $b ]
7then
8 echo "a 大于 b"
9elif [ $a -lt $b ]
10then
11 echo "a 小于 b"
12else
13 echo "没有符合的条件"
14fi
15
16
循环
-
for循环
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
2for loop in ${array[*]}
3do
4 echo "The value is: $loop"
5done
6#或者
7for loop in 1 2 3 4 5
8do
9 echo "The value is: $loop"
10done
11# 但是以下不行
12for loop in (1 2 3 4 5)
13do
14 echo "The value is: $loop"
15done
16
17
-
while循环
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2int=1
3while(( $int<=5 ))
4do
5 echo $int
6 let "int++"
7done
8
9
-
util循环
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3a=0
4
5until [ ! $a -lt 10 ]
6do
7 echo $a
8 a=`expr $a + 1`
9done
10
11
-
无限循环:三种方法
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2do
3 command
4done
5#或者
6while true
7do
8 command
9done
10#或者
11for (( ; ; ))
12do
13 command
14done
15
16
