文章目录
- ArrayList和Vector对比:
- 底层数据结构
- 构造方法
- 扩容机制
- 添加元素
- 删除元素
- 查询
- 迭代器
本来今天是想看一下Stack的源码的,但是在看到Stack的父类结构时
2
3
2
3
我想到了我之前还没怎么看过Vector的源码,甚至乎还很少用,我之前对他的了解大概就是停留在跟ArrayList很相似,是线程安全的ArrayList,先总结下ArrayList和Vector的不同之处,然后带着结论去看源码,找原因
ArrayList源码分析
ArrayList和Vector对比:
-
相同之处:
-
都是基于数组
- 都支持随机访问
- 默认容量都是10
- 都支持动态扩容
- 都支持fail—fast机制
-
不同之处:
-
Vector历史比ArrayList久远,Vector是jdk1.0,ArrayList是jdk1.2
- Vector是线程安全的,ArrayList线程不安全
- Vector动态扩容默认扩容两倍,ArrayList是1.5倍
底层数据结构
Vector底层是基于数组实现的
2
3
2
3
ArrayList底层数据结构也是数组
2
3
2
3
其他相关属性
2
3
4
5
6
2 protected int elementCount;
3 //增长量
4 protected int capacityIncrement;
5
6
构造方法
无参构造,数组容量默认是10
2
3
4
5
6
2 public Vector() {
3 this(10);
4 }
5
6
ArrayList默认数组容量也是10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2 private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
3
4 //构造指定容量的数组(10)
5 public ArrayList() {
6 this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
7 }
8
9
Vcetor其他构造方法:
指定容量和增长量构造
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
2 public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
3 super();
4 if (initialCapacity < 0)
5 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
6 initialCapacity);
7 //构造指定容量的数组
8 this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
9 //设置增长量
10 this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
11 }
12
13
指定容量和增长量为0的构造:
2
3
4
5
2 this(initialCapacity, 0);
3 }
4
5
传入指定集合构造
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2 //转成数组,赋值
3 elementData = c.toArray();
4 elementCount = elementData.length;
5 // c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
6 //如果不是Object[],要重建数组
7 if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
8 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, Object[].class);
9 }
10
11
扩容机制
在了解添加元素之前我们需要理清Vector的扩容机制是怎样的,其实跟ArrayList的扩容机制也很相似
1.计算最小容量:
最小容量 = 当前数组元素数量 + 1,此举的目的就是判断是否需要扩容,最小容量就是相当于成功添加了一个元素后的新的数组元素数量,如果这个新的数组元素数量大于数组长度,那么肯定需要扩容
2
3
4
5
6
7
2 // overflow-conscious code
3 if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
4 grow(minCapacity);
5 }
6
7
2.传入最小容量开始扩容:
-
如果当前数组的增长量 > 0则新数组容量 = 旧数组容量 + 增长量
-
否则,则新数组容量 = 2 * 旧数组容量
-
求出新数组容量后,如果新数组容量 < 最小容量,那么新数组容量 = 最小容量
-
如果新数组容量 > 最大数组容量,则新数组容量 = 整数最大值
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
2 private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
3
4 //扩容
5 private void grow(int minCapacity) {
6 //旧的数组容量
7 int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
8 //新数组容量
9 //如果当前数组的增长量 > 0则新数组容量 = 旧数组容量 + 增长量
10 //否则,则新数组容量 = 2 * 旧数组容量
11 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
12 capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
13 //求出新数组容量后,如果新数组容量 < 最小容量,那么新数组容量 = 最小容量
14 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
15 newCapacity = minCapacity;
16 //如果新数组容量 > 最大数组容量,则新数组容量 = 整数最大值
17 if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
18 newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
19 //真正扩容,实际上就是数组的复制和移动
20 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
21 }
22
23 //判断是取最大数组容量还是整数最大值
24 private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
25 if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
26 throw new OutOfMemoryError();
27 return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
28 Integer.MAX_VALUE :
29 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
30 }
31
32
4.扩容实际:数组复制和移动
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
3 T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class)
4 ? (T[]) new Object[newLength]
5 : (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength);
6 //params0:original:原数组
7 //param1:srcPos:原数组开始位置
8 //param2:copy:新数组
9 //param3:destPost:新数组开始位置
10 //param4:copyLength:要copy的数组的长度
11 System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
12 Math.min(original.length, newLength));
13 return copy;
14 }
15
16
ArrayList的扩容机制其实和Vector很相似,至少原理是一致的,但是在扩容大小上不一样
因为ArrayList没有增长量这一概念,所以ArrayList默认扩容1.5倍
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
2 // 原来的数组容量 = 数组长度
3 int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
4 // 新的数组容量 = 原数组容量+原数组容量/2
5 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
6 //判断下传进来的最小容量 (最小容量 = 当前数组元素数目 + 1)
7 // 如果比当前新数组容量小,则使用最容量
8 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
9 newCapacity = minCapacity;
10 //如果判断当前新容量是否超过最大的数组容量 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8
11 if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
12 newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
13 //开始扩容
14 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
15 }
16
17 //如果判断当前新容量是否超过最大的数组容量 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8
18 private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
19 if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
20 throw new OutOfMemoryError();
21 //如果超多最大数组容量则使用Integer的最大数值,否则还是使用最大数组容量
22 return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
23 Integer.MAX_VALUE :
24 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
25 }
26
27
ArrayList扩容流程:
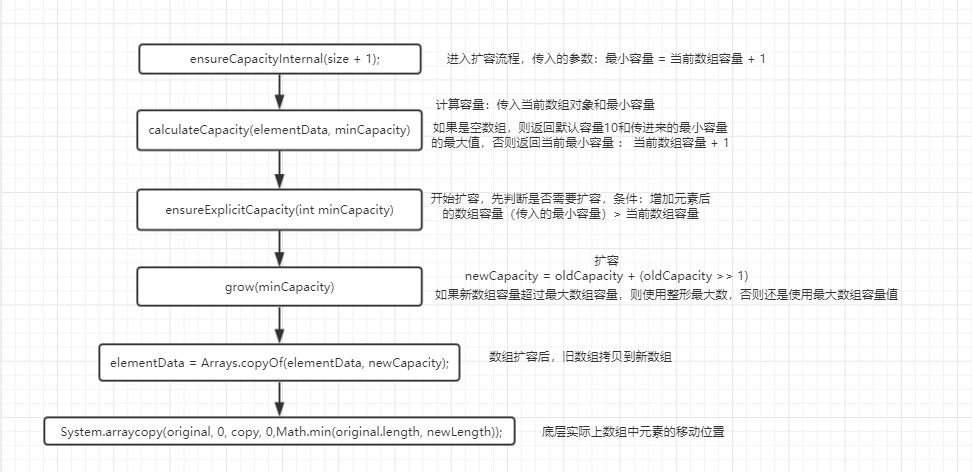
添加元素
数组尾部添加指定元素
可以看到添加方法上带有synchronized同步关键字,保证了在添加元素时的线程安全,但是也会带来获取锁和释放锁的效率问题
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2 modCount++;
3 //判断是否需要扩容
4 ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
5 //直接根据下标添加
6 elementData[elementCount++] = obj;
7 }
8
9
指定位置添加指定元素
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
2 modCount++;
3 if (index > elementCount) {
4 throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index
5 + " > " + elementCount);
6 }
7 //判断是否需要扩容
8 ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
9 //数组移动和复制,腾出index位置 index后的元素向后移动一位
10 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, elementCount - index);
11 //下标添加
12 elementData[index] = obj;
13 //元素数量+1
14 elementCount++;
15 }
16
17
添加指定集合
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2 modCount++;
3 Object[] a = c.toArray();
4 int numNew = a.length;
5 ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + numNew);
6 //扩容,复制到数组后面
7 System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, elementCount, numNew);
8 elementCount += numNew;
9 return numNew != 0;
10 }
11
12
删除元素
删除指定下标元素
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
2 modCount++;
3 if (index >= elementCount)
4 throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
5 //原来该下标对应的元素值
6 E oldValue = elementData(index);
7 //index后面元素的数量
8 int numMoved = elementCount - index - 1;
9 //如果该元素不是最后一个元素
10 if (numMoved > 0)
11 //该元素后面的元素向前移动一位,覆盖删除
12 System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
13 numMoved);
14 //数组最后多余的一位为null,gc
15 elementData[--elementCount] = null; // Let gc do its work
16
17 return oldValue;
18 }
19
20 //和上边方法其实思路是一样的
21 public synchronized void removeElementAt(int index) {
22 modCount++;
23 //检查
24 if (index >= elementCount) {
25 throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
26 elementCount);
27 }
28 else if (index < 0) {
29 throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
30 }
31 int j = elementCount - index - 1;
32 if (j > 0) {
33 //该元素后面的元素向前移动一位,覆盖删除
34 System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, j);
35 }
36 //数组最后多余的一位为null,gc
37 elementCount--;
38 elementData[elementCount] = null; /* to let gc do its work */
39 }
40
41
删除指定元素
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
2 modCount++;
3 //找到该元素下标
4 int i = indexOf(obj);
5 if (i >= 0) {
6 //下标正确则根据下标删除
7 removeElementAt(i);
8 return true;
9 }
10 return false;
11 }
12
13
删除所有元素
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2 modCount++;
3 //循环删除每一个元素,gc
4 for (int i = 0; i < elementCount; i++)
5 elementData[i] = null;
6
7 elementCount = 0;
8 }
9
10
删除指定范围的元素
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2 modCount++;
3 //原理还是数组的移动,将toIndex后的元素向前移动 toIndex - fromIndex
4 int numMoved = elementCount - toIndex;
5 System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex,
6 numMoved);
7
8 // Let gc do its work
9 int newElementCount = elementCount - (toIndex-fromIndex);
10 while (elementCount != newElementCount)
11 elementData[--elementCount] = null;
12 }
13
14
查询
从指定下标开始找到指定元素第一次出现的下标
从前往后找
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2 if (o == null) {
3 for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
4 if (elementData[i]==null)
5 return i;
6 } else {
7 for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
8 if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
9 return i;
10 }
11 return -1;
12 }
13
14
从后往前找
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
2 if (index >= elementCount)
3 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= "+ elementCount);
4
5 if (o == null) {
6 for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
7 if (elementData[i]==null)
8 return i;
9 } else {
10 for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
11 if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
12 return i;
13 }
14 return -1;
15 }
16
17
返回指定下标的元素
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2 return (E) elementData[index];
3 }
4
5 public synchronized E get(int index) {
6 if (index >= elementCount)
7 throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
8
9 return elementData(index);
10 }
11
12
是否包含指定元素
2
3
4
5
6
2 public boolean contains(Object o) {
3 return indexOf(o, 0) >= 0;
4 }
5
6
迭代器
迭代器和ArrayList相比是差不多的,包括实现也是,可以参考ArrayList源码分析
