一、RPC简介
RPC,全称为Remote Procedure Call,即远程过程调用,它是一个计算机通信协议。它允许像调用本地服务一样调用远程服务。它可以有不同的实现方式。如RMI(远程方法调用)、Hessian、Http invoker等。另外,RPC是与语言无关的。
RPC示意图
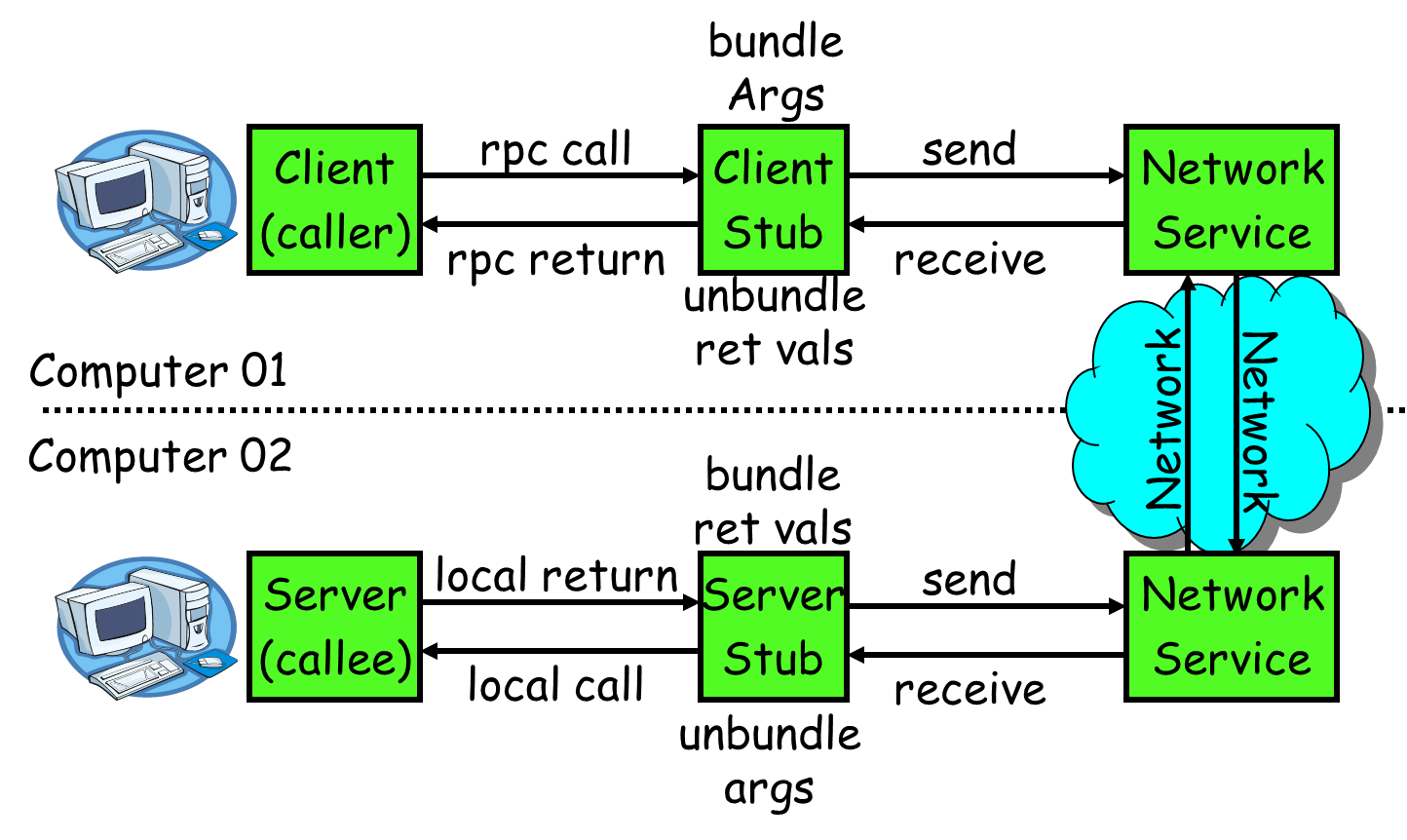
如上图所示,假设Computer1在调用sayHi()方法,对于Computer1而言调用sayHi()方法就像调用本地方法一样,调用 –>返回。但从后续调用可以看出Computer1调用的是Computer2中的sayHi()方法,RPC屏蔽了底层的实现细节,让调用者无需关注网络通信,数据传输等细节。
二、RPC框架的实现
上面介绍了RPC的核心原理:
RPC能够让本地应用简单、高效地调用服务器中的过程(服务)。它主要应用在分布式系统。如Hadoop中的IPC组件。但怎样实现一个RPC框架呢?
从下面几个方面思考,仅供参考:
1.通信模型:假设通信的为A机器与B机器,A与B之间有通信模型,在Java中一般基于BIO或NIO;。
2.过程(服务)定位:使用给定的通信方式,与确定IP与端口及方法名称确定具体的过程或方法;
3.远程代理对象:本地调用的方法(服务)其实是远程方法的本地代理,因此可能需要一个远程代理对象,对于Java而言,远程代理对象可以使用Java的动态对象实现,封装了调用远程方法调用;
4.序列化,将对象名称、方法名称、参数等对象信息进行网络传输需要转换成二进制传输,这里可能需要不同的序列化技术方案。如:protobuf,Arvo等。
三、Java实现RPC框架
1、实现技术方案
下面使用比较原始的方案实现RPC框架,采用Socket通信、动态代理与反射与Java原生的序列化。
2、RPC框架架构
RPC架构分为三部分:
1)服务提供者,运行在服务器端,提供服务接口定义与服务实现类。
2)服务中心,运行在服务器端,负责将本地服务发布成远程服务,管理远程服务,提供给服务消费者使用。
3)服务消费者,运行在客户端,通过远程代理对象调用远程服务。
3、 具体实现
服务提供者接口定义与实现,代码如下:
2
3
4
5
6
2
3 String sayHi(String name);
4
5}
6
HelloServices接口实现类:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3 public String sayHi(String name) {
4 return "Hi, " + name;
5 }
6
7}
8
服务中心代码实现,代码如下:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2 public void stop();
3
4 public void start() throws IOException;
5
6 public void register(Class serviceInterface, Class impl);
7
8 public boolean isRunning();
9
10 public int getPort();
11}
12
服务中心实现类:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
2 private static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
3
4 private static final HashMap<String, Class> serviceRegistry = new HashMap<String, Class>();
5
6 private static boolean isRunning = false;
7
8 private static int port;
9
10 public ServiceCenter(int port) {
11 this.port = port;
12 }
13
14 public void stop() {
15 isRunning = false;
16 executor.shutdown();
17 }
18
19 public void start() throws IOException {
20 ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket();
21 server.bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
22 System.out.println("start server");
23 try {
24 while (true) {
25 // 1.监听客户端的TCP连接,接到TCP连接后将其封装成task,由线程池执行
26 executor.execute(new ServiceTask(server.accept()));
27 }
28 } finally {
29 server.close();
30 }
31 }
32
33 public void register(Class serviceInterface, Class impl) {
34 serviceRegistry.put(serviceInterface.getName(), impl);
35 }
36
37 public boolean isRunning() {
38 return isRunning;
39 }
40
41 public int getPort() {
42 return port;
43 }
44
45 private static class ServiceTask implements Runnable {
46 Socket clent = null;
47
48 public ServiceTask(Socket client) {
49 this.clent = client;
50 }
51
52 public void run() {
53 ObjectInputStream input = null;
54 ObjectOutputStream output = null;
55 try {
56 // 2.将客户端发送的码流反序列化成对象,反射调用服务实现者,获取执行结果
57 input = new ObjectInputStream(clent.getInputStream());
58 String serviceName = input.readUTF();
59 String methodName = input.readUTF();
60 Class<?>[] parameterTypes = (Class<?>[]) input.readObject();
61 Object[] arguments = (Object[]) input.readObject();
62 Class serviceClass = serviceRegistry.get(serviceName);
63 if (serviceClass == null) {
64 throw new ClassNotFoundException(serviceName + " not found");
65 }
66 Method method = serviceClass.getMethod(methodName, parameterTypes);
67 Object result = method.invoke(serviceClass.newInstance(), arguments);
68
69 // 3.将执行结果反序列化,通过socket发送给客户端
70 output = new ObjectOutputStream(clent.getOutputStream());
71 output.writeObject(result);
72 } catch (Exception e) {
73 e.printStackTrace();
74 } finally {
75 if (output != null) {
76 try {
77 output.close();
78 } catch (IOException e) {
79 e.printStackTrace();
80 }
81 }
82 if (input != null) {
83 try {
84 input.close();
85 } catch (IOException e) {
86 e.printStackTrace();
87 }
88 }
89 if (clent != null) {
90 try {
91 clent.close();
92 } catch (IOException e) {
93 e.printStackTrace();
94 }
95 }
96 }
97
98 }
99 }
100}
101
客户端的远程代理对象:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
2 public static <T> T getRemoteProxyObj(final Class<?> serviceInterface, final InetSocketAddress addr) {
3 // 1.将本地的接口调用转换成JDK的动态代理,在动态代理中实现接口的远程调用
4 return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(serviceInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class<?>[]{serviceInterface},
5 new InvocationHandler() {
6 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
7 Socket socket = null;
8 ObjectOutputStream output = null;
9 ObjectInputStream input = null;
10 try {
11 // 2.创建Socket客户端,根据指定地址连接远程服务提供者
12 socket = new Socket();
13 socket.connect(addr);
14
15 // 3.将远程服务调用所需的接口类、方法名、参数列表等编码后发送给服务提供者
16 output = new ObjectOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
17 output.writeUTF(serviceInterface.getName());
18 output.writeUTF(method.getName());
19 output.writeObject(method.getParameterTypes());
20 output.writeObject(args);
21
22 // 4.同步阻塞等待服务器返回应答,获取应答后返回
23 input = new ObjectInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
24 return input.readObject();
25 } finally {
26 if (socket != null) socket.close();
27 if (output != null) output.close();
28 if (input != null) input.close();
29 }
30 }
31 });
32 }
33}
34
最后为测试类:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
4 new Thread(new Runnable() {
5 public void run() {
6 try {
7 Server serviceServer = new ServiceCenter(8088);
8 serviceServer.register(HelloService.class, HelloServiceImpl.class);
9 serviceServer.start();
10 } catch (IOException e) {
11 e.printStackTrace();
12 }
13 }
14 }).start();
15 HelloService service = RPCClient.getRemoteProxyObj(HelloService.class, new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8088));
16 System.out.println(service.sayHi("test"));
17 }
18}
19
运行结果:
2
3
4
2start server
3Hi, test
4
四、总结
RPC本质为消息处理模型,RPC屏蔽了底层不同主机间的通信细节,让进程调用远程的服务就像是本地的服务一样。
五、可以改进的地方
这里实现的简单RPC框架是使用Java语言开发,与Java语言高度耦合,并且通信方式采用的Socket是基于BIO实现的,IO效率不高,还有Java原生的序列化机制占内存太多,运行效率也不高。可以考虑从下面几种方法改进。
- 可以采用基于JSON数据传输的RPC框架;
- 可以使用NIO或直接使用Netty替代BIO实现;
- 使用开源的序列化机制,如Hadoop Avro与Google protobuf等;
- 服务注册可以使用Zookeeper进行管理,能够让应用更加稳定。
