概要
Caffeine是使用Java8对Guava缓存的重写版本,在Spring Boot 2.0中将取代Guava。如果出现Caffeine,CaffeineCacheManager将会自动配置。caffeine是目前最高性能的java本地缓存库。
github:
caffeine介绍
1. 填充策略
1.1 手动加载
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2CaffeineSpec spec = CaffeineSpec.parse(caffeineSpec);
3Caffeine caffeine = Caffeine.from(spec);
4Cache manualCache = caffeine.build();
5// 通过key查询value,没有返回null
6manualCache.getIfPresent("key");
7// 通过key查询value,没有根据传入的function初始化这个key
8manualCache.get("key", k -> load(k));
9// 将key及对应的value放入缓存
10manualCache.put("key", "value");
11// 删除key对应的mapping
12manualCache.invalidate("key");
13
14
通过手动加载你可以显式的去查询、更新、删除一个缓存,Caffeine 的创建方式除了上述方式,还可通过以下方式创建
2
3
4
5
2 .expireAfterWrite(1, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
3 .maximumSize(100)
4
5
1.2 同步加载
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2CaffeineSpec spec = CaffeineSpec.parse(caffeineSpec);
3Caffeine caffeine = Caffeine.from(spec);
4// CacheLoader cacheLoader = key -> load(key);
5CacheLoader cacheLoader = new CacheLoader() {
6 @CheckForNull
7 @Override
8 public Object load(@Nonnull Object key) throws Exception {
9 return load(key);
10 }
11};
12LoadingCache loadingCache = caffeine.build(cacheLoader);
13// 通过key查询value,没有则调用load方法初始化这个key
14loadingCache.get("key");
15List<String> keyList = Arrays.asList("key1", "key2");
16loadingCache.getAll(keyList);
17
18
LoadingCache 通过指定一个 CacheLoader 来构建一个之前不存在的缓存,通过get方法获取缓存时调用load方法来初始化,我们也可以通过getAll批量获取缓存,默认情况下,getAll将会对缓存中没有值的key分别调用load方法,通过重写CacheLoader 中的loadAll方法提高效率。
1.3 异步加载
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
2CaffeineSpec spec = CaffeineSpec.parse(caffeineSpec);
3Caffeine caffeine = Caffeine.from(spec);
4// CacheLoader cacheLoader = key -> load(key);
5CacheLoader cacheLoader = new CacheLoader() {
6 @CheckForNull
7 @Override
8 public Object load(@Nonnull Object key) throws Exception {
9 return load(key);
10 }
11};
12AsyncCacheLoader asyncCacheLoader = new AsyncCacheLoader() {
13 @Nonnull
14 @Override
15 public CompletableFuture asyncLoad(@Nonnull Object key, @Nonnull Executor executor) {
16 return asyncLoad(key);
17 }
18};
19AsyncLoadingCache asyncLoadingCache = caffeine.buildAsync(cacheLoader);
20// 通过key查询value,没有则调用load方法初始化这个key
21asyncLoadingCache.get("key").thenAccept(value -> handle(value));
22List<String> keyList = Arrays.asList("key1", "key2");
23asyncLoadingCache.getAll(keyList).thenAccept(value -> handle(value));
24
25
AsyncLoadingCache 与 LoadingCache 是两个完全独立的接口,caffeine通过调用buildAsync来创建异步的cache,buildAsync有两个重载的方法
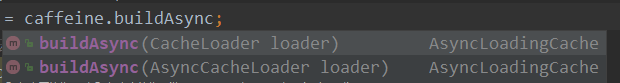
CacheLoader 继承自 AsyncCacheLoader,两种cacheLoader的用法暂时还没有比较清晰的认识,异步加载使用Executor去调用方法并返回一个CompletableFuture,我们拿到这个CompletableFuture可以对其做我们需要的操作。
异步加载默认使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()来执行异步线程,我们可以通过Caffeine.executor(Executor) 方法来替换线程池。
2. 驱逐策略
2.1 基于大小回收
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2 @CheckForNull
3 @Override
4 public Object load(@Nonnull Object key) throws Exception {
5 return load(key);
6 }
7 };
8// 根据缓存的数量进行驱逐
9Caffeine.newBuilder().maximumSize(10).build(cacheLoader);
10// 根据权重进行驱逐
11Caffeine.newBuilder().maximumWeight(10)
12 .weigher((key, value) -> Integer.valueOf(key.toString()))
13 .build(cacheLoader);
14
15
基于大小的回收策略分为两种:
- 当缓存的数量超过配置的缓存大小限制时会发生回收
- 当缓存的总权重超过配置的权重大小限制时会发生回收,我们可以通过weigher方法来指定每个缓存权重的计算方式。
2.2 基于时间回收
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
2Caffeine.newBuilder()
3 .expireAfterAccess(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
4 .build(cacheLoader);
5// 写入后过期
6Caffeine.newBuilder()
7 .expireAfterWrite(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
8 .build(cacheLoader);
9//自定义过期策略
10Caffeine.newBuilder().expireAfter(new Expiry<Object, Object>() {
11 @Override
12 public long expireAfterCreate(
13 Object key, Object value, long currentTime) {
14 return 10;
15 }
16 @Override
17 public long expireAfterUpdate(
18 Object key, Object value, long currentTime, long currentDuration) {
19 return 10;
20 }
21 @Override
22 public long expireAfterRead(
23 Object key, Object value, long currentTime, long currentDuration) {
24 return 10;
25 }
26}).build(cacheLoader);
27
28
基于时间的回收策略分为三种:
- 访问后过期:自上次读或者写算起
- 写入后过期:自上次写算起
- 自定义:自定义过期策略
expireAfterWrite和expireAfterAccess同时存在时,以expireAfterWrite为准。
2.3基于引用回收
2
3
4
5
6
2 .weakKeys()
3 .weakValues()
4 .build(cacheLoader);
5
6
关于强引用、软引用、弱引用、虚引用的详细描述可参考《深入理解jvm虚拟机》这本书,在caffeine中的应用就是你可以指定key、value为软引用,在jvm内存不足时进行回收。
3.刷新策略
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
2 @CheckForNull
3 @Override
4 public Object load(@Nonnull Object key) throws Exception {
5 return load(key);
6 }
7
8 @CheckForNull
9 @Override
10 public Object reload(@Nonnull Object key, @Nonnull Object oldValue) throws Exception {
11 return load(key);
12 }
13};
14Caffeine.newBuilder()
15 .expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
16 .expireAfterAccess(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
17 .build(cacheLoader);
18Caffeine.newBuilder()
19 .executor(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<>()));
20
21
22
我们可以通过expireAfterWrite跟expireAfterAccess来指定刷新时机,当两个参数同时指定时,数据将在具备刷新条件时才去刷新。
caffeine的刷新通过异步调用CacheLoader接口中的reload方法来实现,reload方法的默认实现是通过调用load方法来刷新,当然我们也可以通过重写reload方法来自定义刷新逻辑。
由于刷新是通过ForkJoinPool.commonPool()来异步调用,所以触发刷新的线程会直接拿到旧数据返回,我们可以使用executor指定的线程池替换ForkJoinPool.commonPool()。
spring boot + caffeine
1.引入依赖
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
3 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
4</dependency>
5<dependency>
6 <groupId>com.github.ben-manes.caffeine</groupId>
7 <artifactId>caffeine</artifactId>
8 <version>2.6.2</version>
9</dependency>
10
11
2.配置caffeine
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
2@EnableCaching
3public class CaffeineConfig {
4
5 private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CaffeineConfig.class);
6
7 @Autowired
8 private ConfigureParameter configureParameter;
9
10 /**
11 * caffeine CacheManager
12 * @return
13 */
14 @Bean("caffeine")
15 public CacheManager cacheManager() {
16 String caffeineSpec = configureParameter.getCaffeineSpec();
17 CaffeineSpec spec = CaffeineSpec.parse(caffeineSpec);
18 Caffeine caffeine = Caffeine.from(spec);
19 CaffeineCacheManager cacheManager = new CaffeineCacheManager();
20 cacheManager.setCaffeine(caffeine);
21 cacheManager.setAllowNullValues(false);
22 CacheLoader<Object, Object> cacheLoader = key -> null;
23 cacheManager.setCacheLoader(cacheLoader);
24 return cacheManager;
25 }
26
27}
28
29
在上例中我们通过caffeineSpec来构建caffeine对象,并且CacheLoade中的load方法我们直接返回了一个null,这是为了让spring去调用原方法,来初始化caffeine缓存,这个在之后的源码分析中会提到,我们并没有去重写reload方法,这时候默认去调用load方法,而load返回null,所以注意在异步刷新的时候caffeine会把这个null放置到caffeine缓存中,在caffeine中并没有找到控制value是否可为null的配置,但是spring为我们提供了一个方法setAllowNullValues,如果为false不允许value为null,则在value为null时会抛出一个异常。
我们也可以通过SimpleCacheManage的方式来让spring管理caffeine
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2 * caffeine CacheManager
3 * @return
4 */
5 @Bean("caffeine")
6 public CacheManager cacheManager() {
7 String groupInfo = Constant.GROUP_INFO;
8 CacheLoader cacheLoader = cacheLoaderContext.getCacheLoader(groupInfo);
9 SimpleCacheManager simpleCacheManager = new SimpleCacheManager();
10 List<CaffeineCache> cacheList = new ArrayList<>();
11 String caffeineSpec = configureParameter.getCaffeineSpec();
12 CaffeineSpec spec = CaffeineSpec.parse(caffeineSpec);
13 Caffeine caffeine = Caffeine.from(spec);
14 CaffeineCache caffeineCache = new CaffeineCache(groupInfo, caffeine.build(cacheLoader) , false);
15 cacheList.add(caffeineCache);
16 simpleCacheManager.setCaches(cacheList);
17 return simpleCacheManager;
18 }
19
20
CaffeineCache构造器的第三个参数是allowNullValues,不过这个参数我测试并没有限制到value是否允许为null
3.使用注解
2
3
2
3
我们可以使用spring提供的@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict等注解来方便的使用caffeine缓存。
如果使用了多个cahce,比如redis、caffeine等,必须指定某一个CacheManage为@primary,在@Cacheable注解中没指定cacheManager 则使用标记为primary的那个。
4.CacheAspectSupport
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
2 // 是否异步 sync = true/false
3 if (contexts.isSynchronized()) {
4 CacheOperationContext context = contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class).iterator().next();
5 if (isConditionPassing(context, CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT)) {
6 Object key = generateKey(context, CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT);
7 Cache cache = context.getCaches().iterator().next();
8 try {
9 return wrapCacheValue(method, cache.get(key, new Callable<Object>() {
10 @Override
11 public Object call() throws Exception {
12 return unwrapReturnValue(invokeOperation(invoker));
13 }
14 }));
15 }
16 catch (Cache.ValueRetrievalException ex) {
17 // The invoker wraps any Throwable in a ThrowableWrapper instance so we
18 // can just make sure that one bubbles up the stack.
19 throw (CacheOperationInvoker.ThrowableWrapper) ex.getCause();
20 }
21 }
22 else {
23 // No caching required, only call the underlying method
24 return invokeOperation(invoker);
25 }
26 }
27
28
29 // Process any early evictions
30 processCacheEvicts(contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class), true,
31 CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT);
32
33 // 真正的去调用底层cache,获取value
34 Cache.ValueWrapper cacheHit = findCachedItem(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class));
35
36 // Collect puts from any @Cacheable miss, if no cached item is found
37 List<CachePutRequest> cachePutRequests = new LinkedList<CachePutRequest>();
38 if (cacheHit == null) {
39 collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class),
40 CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT, cachePutRequests);
41 }
42
43 Object cacheValue;
44 Object returnValue;
45
46 if (cacheHit != null && cachePutRequests.isEmpty() && !hasCachePut(contexts)) {
47 // If there are no put requests, just use the cache hit
48 cacheValue = cacheHit.get();
49 returnValue = wrapCacheValue(method, cacheValue);
50 }
51 // 这里如果底层cache的返回值为null,spring会去调用原方法
52 else {
53 // Invoke the method if we don't have a cache hit
54 returnValue = invokeOperation(invoker);
55 cacheValue = unwrapReturnValue(returnValue);
56 }
57
58 // Collect any explicit @CachePuts
59 collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CachePutOperation.class), cacheValue, cachePutRequests);
60
61 // 并将获取到的value放置到底层cache中
62 for (CachePutRequest cachePutRequest : cachePutRequests) {
63 cachePutRequest.apply(cacheValue);
64 }
65
66 // Process any late evictions
67 processCacheEvicts(contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class), false, cacheValue);
68
69 return returnValue;
70 }
71
72
73
CacheAspectSupport是spring提供的与三方cache整合的一个重要类,若想了解更详细的底层实现可以去阅读下源码。
