在前面的博文中,介绍一些消息分割的方案,以及MINA、Netty、Twisted针对这些方案提供的相关API。例如MINA的TextLineCodecFactory、PrefixedStringCodecFactory,Netty的LineBasedFrameDecoder、LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder,Twisted的LineOnlyReceiver、Int32StringReceiver。
除了这些方案,还有很多其他方案,当然也可以自己定义。在这里,我们定制一个自己的方案,并分别使用MINA、Netty、Twisted实现对这种消息的解析和组装,也就是编码和解码。
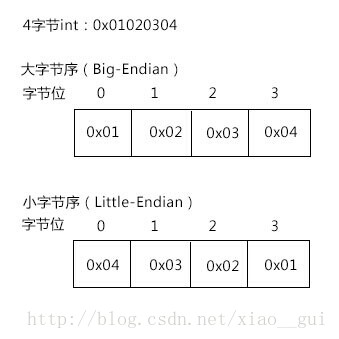
上一篇博文中介绍了一种用固定字节数的Header来指定Body字节数的消息分割方案,其中Header部分是常规的**大字节序(Big-Endian)的4字节整数。本文中对这个方案稍作修改,将固定字节数的Header改为小字节序(Little-Endian)**的4字节整数。
常规的大字节序表示一个数的话,用高字节位的存放数字的低位,比较符合人的习惯。而小字节序和大字节序正好相反,用高字节位存放数字的高位。
Python中struct模块支持大小字节序的pack和unpack,在Java中可以用下面的两个方法实现小字节序字节数组转int和int转小字节序字节数组,下面的Java程序中将会用到这两个方法:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
2
3 /**
4 * 将int转成4字节的小字节序字节数组
5 */
6 public static byte[] toLittleEndian(int i) {
7 byte[] bytes = new byte[4];
8 bytes[0] = (byte) i;
9 bytes[1] = (byte) (i >>> 8);
10 bytes[2] = (byte) (i >>> 16);
11 bytes[3] = (byte) (i >>> 24);
12 return bytes;
13 }
14
15 /**
16 * 将小字节序的4字节的字节数组转成int
17 */
18 public static int getLittleEndianInt(byte[] bytes) {
19 int b0 = bytes[0] & 0xFF;
20 int b1 = bytes[1] & 0xFF;
21 int b2 = bytes[2] & 0xFF;
22 int b3 = bytes[3] & 0xFF;
23 return b0 + (b1 << 8) + (b2 << 16) + (b3 << 24);
24 }
25}
26
无论是MINA、Netty还是Twisted,消息的编码、解码、切合的代码,都是应该和业务逻辑代码分开,这样有利于代码的开发、重用和维护。在MINA和Netty中类似,编码、解码需要继承实现相应的Encoder、Decoder,而在Twisted中则是继承Protocol实现编码解码。虽然实现方式不同,但是它们的功能都是一样的:
1、对消息根据一定规则进行切合,例如固定长度消息、按行、按分隔符、固定长度Header指定Body长度等;
2、将切合后的消息由字节码转成自己想要的类型,如MINA中将IoBuffer转成字符串,这样messageReceived接收到的message参数就是String类型;
3、write的时候可以传入自定义类型的参数,由编码器完成编码。
下面分别用MINA、Netty、Twisted实现4字节的小字节序int来指定body长度的消息的编码解码。
MINA:
在MINA中对接收到的消息进行切合和解码,一般会定义一个解码器类,继承自抽象类CumulativeProtocolDecoder,实现doDecode方法:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
2
3 @Override
4 protected boolean doDecode(IoSession session, IoBuffer in, ProtocolDecoderOutput out) throws Exception {
5
6 // 如果没有接收完Header部分(4字节),直接返回false
7 if(in.remaining() < 4) {
8 return false;
9 } else {
10
11 // 标记开始位置,如果一条消息没传输完成则返回到这个位置
12 in.mark();
13
14 byte[] bytes = new byte[4];
15 in.get(bytes); // 读取4字节的Header
16
17 int bodyLength = LittleEndian.getLittleEndianInt(bytes); // 按小字节序转int
18
19 // 如果body没有接收完整,直接返回false
20 if(in.remaining() < bodyLength) {
21 in.reset(); // IoBuffer position回到原来标记的地方
22 return false;
23 } else {
24 byte[] bodyBytes = new byte[bodyLength];
25 in.get(bodyBytes);
26 String body = new String(bodyBytes, "UTF-8");
27 out.write(body); // 解析出一条消息
28 return true;
29 }
30 }
31 }
32}
33
另外,session.write的时候要对数据编码,需要定义一个编码器,继承自抽象类ProtocolEncoderAdapter,实现encode方法:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3 @Override
4 public void encode(IoSession session, Object message,
5 ProtocolEncoderOutput out) throws Exception {
6
7 String msg = (String) message;
8 byte[] bytes = msg.getBytes("UTF-8");
9 int length = bytes.length;
10 byte[] header = LittleEndian.toLittleEndian(length); // 按小字节序转成字节数组
11
12 IoBuffer buffer = IoBuffer.allocate(length + 4);
13 buffer.put(header); // header
14 buffer.put(bytes); // body
15 buffer.flip();
16 out.write(buffer);
17 }
18}
19
在服务器启动的时候加入相应的编码器和解码器:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
4 IoAcceptor acceptor = new NioSocketAcceptor();
5
6 // 指定编码解码器
7 acceptor.getFilterChain().addLast("codec",
8 new ProtocolCodecFilter(new MyMinaEncoder(), new MyMinaDecoder()));
9
10 acceptor.setHandler(new TcpServerHandle());
11 acceptor.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
12 }
13}
14
下面是业务逻辑的代码:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
2
3 @Override
4 public void exceptionCaught(IoSession session, Throwable cause)
5 throws Exception {
6 cause.printStackTrace();
7 }
8
9 // 接收到新的数据
10 @Override
11 public void messageReceived(IoSession session, Object message)
12 throws Exception {
13
14 // MyMinaDecoder将接收到的数据由IoBuffer转为String
15 String msg = (String) message;
16 System.out.println("messageReceived:" + msg);
17
18 // MyMinaEncoder将write的字符串添加了一个小字节序Header并转为字节码
19 session.write("收到");
20 }
21}
22
Netty:
Netty中解码器和MINA类似,解码器继承抽象类ByteToMessageDecoder,实现decode方法:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
2
3 @Override
4 protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
5
6 // 如果没有接收完Header部分(4字节),直接退出该方法
7 if(in.readableBytes() >= 4) {
8
9 // 标记开始位置,如果一条消息没传输完成则返回到这个位置
10 in.markReaderIndex();
11
12 byte[] bytes = new byte[4];
13 in.readBytes(bytes); // 读取4字节的Header
14
15 int bodyLength = LittleEndian.getLittleEndianInt(bytes); // header按小字节序转int
16
17 // 如果body没有接收完整
18 if(in.readableBytes() < bodyLength) {
19 in.resetReaderIndex(); // ByteBuf回到标记位置
20 } else {
21 byte[] bodyBytes = new byte[bodyLength];
22 in.readBytes(bodyBytes);
23 String body = new String(bodyBytes, "UTF-8");
24 out.add(body); // 解析出一条消息
25 }
26 }
27 }
28}
29
下面是编码器,继承自抽象类MessageToByteEncoder,实现encode方法:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2
3 @Override
4 protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg, ByteBuf out)
5 throws Exception {
6
7 byte[] bytes = msg.getBytes("UTF-8");
8 int length = bytes.length;
9 byte[] header = LittleEndian.toLittleEndian(length); // int按小字节序转字节数组
10 out.writeBytes(header); // write header
11 out.writeBytes(bytes); // write body
12 }
13}
14
加上相应的编码器和解码器:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
4 EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
5 EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
6 try {
7 ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
8 b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
9 .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
10 .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
11 @Override
12 public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch)
13 throws Exception {
14 ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
15
16 // 加上自己的Encoder和Decoder
17 pipeline.addLast(new MyNettyDecoder());
18 pipeline.addLast(new MyNettyEncoder());
19
20 pipeline.addLast(new TcpServerHandler());
21 }
22 });
23 ChannelFuture f = b.bind(8080).sync();
24 f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
25 } finally {
26 workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
27 bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
28 }
29 }
30}
31
业务逻辑处理类:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2
3 // 接收到新的数据
4 @Override
5 public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
6
7 // MyNettyDecoder将接收到的数据由ByteBuf转为String
8 String message = (String) msg;
9 System.out.println("channelRead:" + message);
10
11 // MyNettyEncoder将write的字符串添加了一个小字节序Header并转为字节码
12 ctx.writeAndFlush("收到");
13 }
14
15 @Override
16 public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
17 cause.printStackTrace();
18 ctx.close();
19 }
20}
21
Twisted:
Twisted的实现方式和MINA、Netty不太一样,其实现方式相对来说更加原始,但是越原始也越接近底层原理。
首先要定义一个MyProtocol类继承自Protocol,用于充当类似于MINA、Netty的编码、解码器。处理业务逻辑的类TcpServerHandle继承MyProtocol,重写或调用MyProtocol提供的一些方法。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
2
3from struct import pack, unpack
4from twisted.internet.protocol import Factory
5from twisted.internet.protocol import Protocol
6from twisted.internet import reactor
7
8# 编码、解码器
9class MyProtocol(Protocol):
10
11 # 用于暂时存放接收到的数据
12 _buffer = b""
13
14 def dataReceived(self, data):
15 # 上次未处理的数据加上本次接收到的数据
16 self._buffer = self._buffer + data
17 # 一直循环直到新的消息没有接收完整
18 while True:
19 # 如果header接收完整
20 if len(self._buffer) >= 4:
21 # 按小字节序转int
22 length, = unpack("<I", self._buffer[0:4])
23 # 如果body接收完整
24 if len(self._buffer) >= 4 + length:
25 # body部分
26 packet = self._buffer[4:4 + length]
27 # 新的一条消息接收并解码完成,调用stringReceived
28 self.stringReceived(packet)
29 # 去掉_buffer中已经处理的消息部分
30 self._buffer = self._buffer[4 + length:]
31 else:
32 break;
33 else:
34 break;
35
36 def stringReceived(self, data):
37 raise NotImplementedError
38
39 def sendString(self, string):
40 self.transport.write(pack("<I", len(string)) + string)
41
42# 逻辑代码
43class TcpServerHandle(MyProtocol):
44
45 # 实现MyProtocol提供的stringReceived而不是dataReceived,不然无法解码
46 def stringReceived(self, data):
47
48 # data为MyProtocol解码后的数据
49 print 'stringReceived:' + data
50
51 # 调用sendString而不是self.transport.write,不然不能进行编码
52 self.sendString("收到")
53
54factory = Factory()
55factory.protocol = TcpServerHandle
56reactor.listenTCP(8080, factory)
57reactor.run()
58
下面是Java编写的一个客户端测试程序:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
4
5 Socket socket = null;
6 OutputStream out = null;
7 InputStream in = null;
8
9 try {
10
11 socket = new Socket("localhost", 8080);
12 out = socket.getOutputStream();
13 in = socket.getInputStream();
14
15 // 请求服务器
16 String data = "我是客户端";
17 byte[] outputBytes = data.getBytes("UTF-8");
18 out.write(LittleEndian.toLittleEndian(outputBytes.length)); // write header
19 out.write(outputBytes); // write body
20 out.flush();
21
22 // 获取响应
23 byte[] inputBytes = new byte[1024];
24 int length = in.read(inputBytes);
25 if(length >= 4) {
26 int bodyLength = LittleEndian.getLittleEndianInt(inputBytes);
27 if(length >= 4 + bodyLength) {
28 byte[] bodyBytes = Arrays.copyOfRange(inputBytes, 4, 4 + bodyLength);
29 System.out.println("Header:" + bodyLength);
30 System.out.println("Body:" + new String(bodyBytes, "UTf-8"));
31 }
32 }
33
34 } finally {
35 // 关闭连接
36 in.close();
37 out.close();
38 socket.close();
39 }
40 }
41}
42
用客户端分别测试上面三个TCP服务器:
MINA服务器输出结果:
*messageReceived:我是客户端
*
Netty服务器输出结果:
*channelRead:我是客户端
*
Twisted服务器输出结果:
*stringReceived:我是客户端
*
客户端测试三个服务器的输出结果都是:
Header:6
Body:收到
由于一个汉字一般占3个字节,所以两个汉字对应的Header为6。
MINA、Netty、Twisted一起学系列
MINA、Netty、Twisted一起学(一):实现简单的TCP服务器
MINA、Netty、Twisted一起学(二):TCP消息边界问题及按行分割消息
MINA、Netty、Twisted一起学(三):TCP消息固定大小的前缀(Header)
MINA、Netty、Twisted一起学(四):定制自己的协议
MINA、Netty、Twisted一起学(五):整合protobuf
MINA、Netty、Twisted一起学(六):session
MINA、Netty、Twisted一起学(七):发布/订阅(Publish/Subscribe)
MINA、Netty、Twisted一起学(八):HTTP服务器
MINA、Netty、Twisted一起学(九):异步IO和回调函数
MINA、Netty、Twisted一起学(十):线程模型
MINA、Netty、Twisted一起学(十一):SSL/TLS
MINA、Netty、Twisted一起学(十二):HTTPS
