HttpBasic和FormLogin都是security的认证方式,这种认证是在用户访问被保护资源时进行登录使用。本节主要讲解如何使用HttpBasic实现认证。
我举个简单的例子,一个商品管理系统中拥有:查看商品,新增商品,修改商品,删除商品这几个功能。借助这些功能使用一下HttpBasic。
1:如图所示,新增一个商品controller
package com.xhc;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
/**
* 商品
*
* @author xuhongchang
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/goods")
public class GoodsController {
/**
* 商品首页
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index() {
return "index";
}
/**
* 商品新增
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/add")
public String add() {
return "goods/addGoods";
}
/**
* 商品修改
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/update")
public String update() {
return "goods/updateGoods";
}
/**
* 商品删除
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/delete")
public String delete() {
return "goods/deleteGoods";
}
/**
* 商品展示
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/list")
public String list() {
return "goods/listGoods";
}
}
2:在springmvc.xml中增加配置。增加后的代码如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:contenxt="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!– 扫描Controller类–>
<contenxt:component-scan base-package="com.xhc"/>
<!–注解方式处理器映射器和处理器适配器 –>
mvc:annotation-driven</mvc:annotation-driven>
<!–视图解析器–>
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<!–前缀 –>
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/>
<!– 后缀–>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
</bean>
</beans>
3:如下图新增jsp/goods文件夹,并新增对应的jsp文件。具体页面代码分别列在下面
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>新增商品</title>
</head>
<body>新增商品页面
</body>
</html><%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>商品删除</title>
</head>
<body>商品删除页面
</body>
</html><%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>显示商品</title>
</head>
<body>显示商品页面
</body>
</html><%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>商品更新</title>
</head>
<body>商品更新页面
</body>
</html><%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>首页</title>
</head>
<body>商品信息管理</br>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/goods/list">商品显示</a></br>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/goods/add">商品添加</a></br>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/goods/update">商品修改</a></br>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/goods/delete">商品删除</a></br>
</body>
</html>
启动项目,访问ip+端口+项目名+goods/index

4:以上是为使用springSecurity做准备。下面讲解一下spring-security.xml文件中标签的含义。
<!– 从标签的名字就可以大致看出各自的作用,具体的使用,下面会介绍到的 –>
<!– security:http主要的主要作用是配置过滤器链1: 保护资源
2: 定义什么角色访问什么样的资源
3: 定义认证方式
4: 定义登录页面,登录请求地址,错误处理等
–>
</security:http>
<!– 认证管理器:认证信息的提供方式,用户名,密码,权限等 –>
security:authentication-manager
</security:authentication-manager>
5:配置Http-basic
修改spring-security.xml文件的security:http标签中的内容,security:http-basic即表示项目使用http-basic方式进行认证。
<!–
pattern:需要拦截的资源。/\*\*表示拦截所有的资源
access:拦截的方式。
isFullyAuthenticated:资源需要认证才能被访问
–>
<security:intercept-url pattern="/**" access="isFullyAuthenticated()"/>
<!– 使用http-basic方式进行认证 –>
</security:http>
重新启动项目进行访问,出现下图,表示配置成功。访问项目资源需要登录。
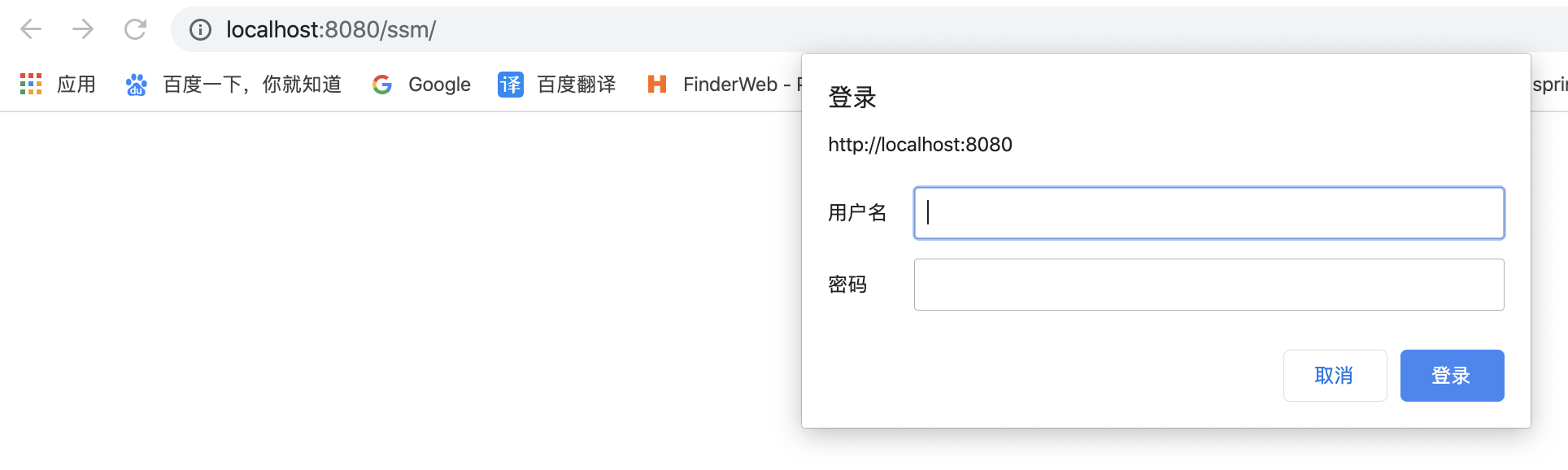
可是用户名和密码从哪里得到呢?
还记得上面说的security:authentication-manager标签吗?修改配置,用户名和密码暂时写死,权限一定要以ROLE_开头。
security:authentication-manager
security:authentication-provider
<security:user name="xhc" password="123456" authorities="ROLE_USER"/>
</security:user-service>
</security:authentication-provider>
</security:authentication-manager>
启动运行,输入用户名密码即可访问资源。
到此,http-basic的配置方式基本完成。但是用户名和密码暂时是写死,后面会将此换成从数据库中读取。稍安勿躁,稍安勿躁。
