本章内容
1、socket
2、IO多路复用
3、socketserver
Socket
socket起源于Unix,而Unix/Linux基本哲学之一就是“一切皆文件”,对于文件用【打开】【读写】【关闭】模式来操作。socket就是该模式的一个实现,socket即是一种特殊的文件,一些socket函数就是对其进行的操作(读/写IO、打开、关闭)
基本上,Socket 是任何一种计算机网络通讯中最基础的内容。例如当你在浏览器地址栏中输入 http://www.cnblogs.com/ 时,你会打开一个套接字,然后连接到 http://www.cnblogs.com/ 并读取响应的页面然后然后显示出来。而其他一些聊天客户端如 gtalk 和 skype 也是类似。任何网络通讯都是通过 Socket 来完成的。
Python 官方关于 Socket 的函数请看 http://docs.python.org/library/socket.html
socket和file的区别:
1、file模块是针对某个指定文件进行【打开】【读写】【关闭】
2、socket模块是针对 服务器端 和 客户端Socket 进行【打开】【读写】【关闭】
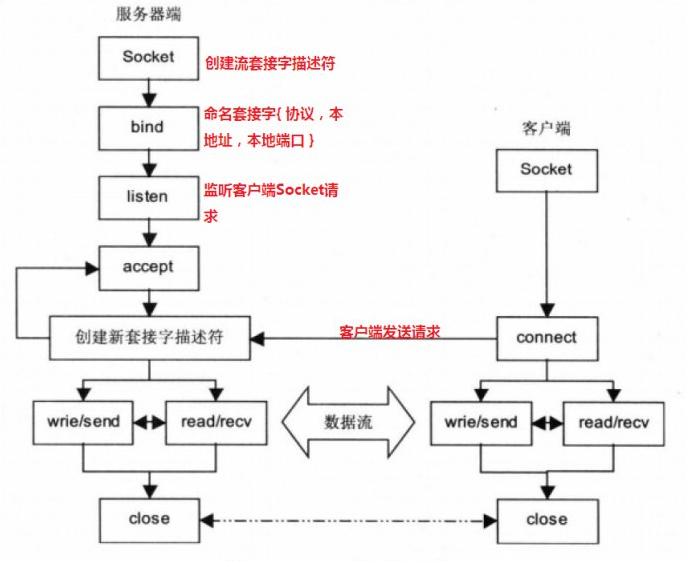
那我们就先来创建一个socket服务端吧
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3sk = socket.socket()
4sk.bind(("127.0.0.1",8080))
5sk.listen(5)
6
7conn,address = sk.accept()
8sk.sendall(bytes("Hello world",encoding="utf-8"))
9
server


2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3obj = socket.socket()
4obj.connect(("127.0.0.1",8080))
5
6ret = str(obj.recv(1024),encoding="utf-8")
7print(ret)
8
View Code
socket更多功能


2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
2 """
3 bind(address)
4
5 Bind the socket to a local address. For IP sockets, the address is a
6 pair (host, port); the host must refer to the local host. For raw packet
7 sockets the address is a tuple (ifname, proto [,pkttype [,hatype]])
8 """
9'''将套接字绑定到本地地址。是一个IP套接字的地址对(主机、端口),主机必须参考本地主机。'''
10 pass
11
12 def close(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
13 """
14 close()
15
16 Close the socket. It cannot be used after this call.
17 """
18 '''关闭socket'''
19 pass
20
21 def connect(self, address): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
22 """
23 connect(address)
24
25 Connect the socket to a remote address. For IP sockets, the address
26 is a pair (host, port).
27 """
28 '''将套接字连接到远程地址。IP套接字的地址'''
29 pass
30
31 def connect_ex(self, address): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
32 """
33 connect_ex(address) -> errno
34
35 This is like connect(address), but returns an error code (the errno value)
36 instead of raising an exception when an error occurs.
37 """
38 pass
39
40 def detach(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
41 """
42 detach()
43
44 Close the socket object without closing the underlying file descriptor.
45 The object cannot be used after this call, but the file descriptor
46 can be reused for other purposes. The file descriptor is returned.
47 """
48'''关闭套接字对象没有关闭底层的文件描述符。'''
49 pass
50
51 def fileno(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
52 """
53 fileno() -> integer
54
55 Return the integer file descriptor of the socket.
56 """
57 '''返回整数的套接字的文件描述符。'''
58 return 0
59
60 def getpeername(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
61 """
62 getpeername() -> address info
63
64 Return the address of the remote endpoint. For IP sockets, the address
65 info is a pair (hostaddr, port).
66 """
67 '''返回远程端点的地址。IP套接字的地址'''
68 pass
69
70 def getsockname(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
71 """
72 getsockname() -> address info
73
74 Return the address of the local endpoint. For IP sockets, the address
75 info is a pair (hostaddr, port).
76 """
77 '''返回远程端点的地址。IP套接字的地址'''
78 pass
79
80 def getsockopt(self, level, option, buffersize=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
81 """
82 getsockopt(level, option[, buffersize]) -> value
83
84 Get a socket option. See the Unix manual for level and option.
85 If a nonzero buffersize argument is given, the return value is a
86 string of that length; otherwise it is an integer.
87 """
88 '''得到一个套接字选项'''
89 pass
90
91 def gettimeout(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
92 """
93 gettimeout() -> timeout
94
95 Returns the timeout in seconds (float) associated with socket
96 operations. A timeout of None indicates that timeouts on socket
97 operations are disabled.
98 """
99 '''返回的超时秒数(浮动)与套接字相关联'''
100 return timeout
101
102 def ioctl(self, cmd, option): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
103 """
104 ioctl(cmd, option) -> long
105
106 Control the socket with WSAIoctl syscall. Currently supported 'cmd' values are
107 SIO_RCVALL: 'option' must be one of the socket.RCVALL_* constants.
108 SIO_KEEPALIVE_VALS: 'option' is a tuple of (onoff, timeout, interval).
109 """
110 return 0
111
112 def listen(self, backlog=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
113 """
114 listen([backlog])
115
116 Enable a server to accept connections. If backlog is specified, it must be
117 at least 0 (if it is lower, it is set to 0); it specifies the number of
118 unaccepted connections that the system will allow before refusing new
119 connections. If not specified, a default reasonable value is chosen.
120 """
121 '''使服务器能够接受连接。'''
122 pass
123
124 def recv(self, buffersize, flags=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
125 """
126 recv(buffersize[, flags]) -> data
127
128 Receive up to buffersize bytes from the socket. For the optional flags
129 argument, see the Unix manual. When no data is available, block until
130 at least one byte is available or until the remote end is closed. When
131 the remote end is closed and all data is read, return the empty string.
132 """
133'''当没有数据可用,阻塞,直到至少一个字节是可用的或远程结束之前关闭。'''
134 pass
135
136 def recvfrom(self, buffersize, flags=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
137 """
138 recvfrom(buffersize[, flags]) -> (data, address info)
139
140 Like recv(buffersize, flags) but also return the sender's address info.
141 """
142 pass
143
144 def recvfrom_into(self, buffer, nbytes=None, flags=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
145 """
146 recvfrom_into(buffer[, nbytes[, flags]]) -> (nbytes, address info)
147
148 Like recv_into(buffer[, nbytes[, flags]]) but also return the sender's address info.
149 """
150 pass
151
152 def recv_into(self, buffer, nbytes=None, flags=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
153 """
154 recv_into(buffer, [nbytes[, flags]]) -> nbytes_read
155
156 A version of recv() that stores its data into a buffer rather than creating
157 a new string. Receive up to buffersize bytes from the socket. If buffersize
158 is not specified (or 0), receive up to the size available in the given buffer.
159
160 See recv() for documentation about the flags.
161 """
162 pass
163
164 def send(self, data, flags=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
165 """
166 send(data[, flags]) -> count
167
168 Send a data string to the socket. For the optional flags
169 argument, see the Unix manual. Return the number of bytes
170 sent; this may be less than len(data) if the network is busy.
171 """
172 '''发送一个数据字符串到套接字。'''
173 pass
174
175 def sendall(self, data, flags=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
176 """
177 sendall(data[, flags])
178
179 Send a data string to the socket. For the optional flags
180 argument, see the Unix manual. This calls send() repeatedly
181 until all data is sent. If an error occurs, it's impossible
182 to tell how much data has been sent.
183 """
184 '''发送一个数据字符串到套接字,直到所有数据发送完成'''
185 pass
186
187 def sendto(self, data, flags=None, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown; NOTE: unreliably restored from __doc__
188 """
189 sendto(data[, flags], address) -> count
190
191 Like send(data, flags) but allows specifying the destination address.
192 For IP sockets, the address is a pair (hostaddr, port).
193 """
194 pass
195
196 def setblocking(self, flag): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
197 """
198 setblocking(flag)
199
200 Set the socket to blocking (flag is true) or non-blocking (false).
201 setblocking(True) is equivalent to settimeout(None);
202 setblocking(False) is equivalent to settimeout(0.0).
203 """
204'''是否阻塞(默认True),如果设置False,那么accept和recv时一旦无数据,则报错。'''
205 pass
206
207 def setsockopt(self, level, option, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
208 """
209 setsockopt(level, option, value)
210
211 Set a socket option. See the Unix manual for level and option.
212 The value argument can either be an integer or a string.
213 """
214 pass
215
216 def settimeout(self, timeout): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
217 """
218 settimeout(timeout)
219
220 Set a timeout on socket operations. 'timeout' can be a float,
221 giving in seconds, or None. Setting a timeout of None disables
222 the timeout feature and is equivalent to setblocking(1).
223 Setting a timeout of zero is the same as setblocking(0).
224 """
225 pass
226
227 def share(self, process_id): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
228 """
229 share(process_id) -> bytes
230
231 Share the socket with another process. The target process id
232 must be provided and the resulting bytes object passed to the target
233 process. There the shared socket can be instantiated by calling
234 socket.fromshare().
235 """
236 return b""
237
238 def shutdown(self, flag): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
239 """
240 shutdown(flag)
241
242 Shut down the reading side of the socket (flag == SHUT_RD), the writing side
243 of the socket (flag == SHUT_WR), or both ends (flag == SHUT_RDWR).
244 """
245 pass
246
247 def _accept(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
248 """
249 _accept() -> (integer, address info)
250
251 Wait for an incoming connection. Return a new socket file descriptor
252 representing the connection, and the address of the client.
253 For IP sockets, the address info is a pair (hostaddr, port).
254 """
255 pass
256
257
更多功能
注:撸主知道大家懒,所以把全部功能的中文标记在每个功能的下面啦。下面撸主列一些经常用到的吧
sk.bind(address)
s.bind(address) 将套接字绑定到地址。address地址的格式取决于地址族。在AF_INET下,以元组(host,port)的形式表示地址。
sk.listen(backlog)
开始监听传入连接。backlog指定在拒绝连接之前,可以挂起的最大连接数量。
backlog等于5,表示内核已经接到了连接请求,但服务器还没有调用accept进行处理的连接个数最大为5
这个值不能无限大,因为要在内核中维护连接队列
sk.setblocking(bool)
是否阻塞(默认True),如果设置False,那么accept和recv时一旦无数据,则报错。
sk.accept()
接受连接并返回(conn,address),其中conn是新的套接字对象,可以用来接收和发送数据。address是连接客户端的地址。
接收TCP 客户的连接(阻塞式)等待连接的到来
sk.connect(address)
连接到address处的套接字。一般,address的格式为元组(hostname,port),如果连接出错,返回socket.error错误。
sk.connect_ex(address)
同上,只不过会有返回值,连接成功时返回 0 ,连接失败时候返回编码,例如:10061
sk.close()
关闭套接字
sk.recv(bufsize[,flag])
接受套接字的数据。数据以字符串形式返回,bufsize指定最多可以接收的数量。flag提供有关消息的其他信息,通常可以忽略。
sk.recvfrom(bufsize[.flag])
与recv()类似,但返回值是(data,address)。其中data是包含接收数据的字符串,address是发送数据的套接字地址。
sk.send(string[,flag])
将string中的数据发送到连接的套接字。返回值是要发送的字节数量,该数量可能小于string的字节大小。即:可能未将指定内容全部发送。
sk.sendall(string[,flag])
将string中的数据发送到连接的套接字,但在返回之前会尝试发送所有数据。成功返回None,失败则抛出异常。
内部通过递归调用send,将所有内容发送出去。
sk.sendto(string[,flag],address)
将数据发送到套接字,address是形式为(ipaddr,port)的元组,指定远程地址。返回值是发送的字节数。该函数主要用于UDP协议。
sk.settimeout(timeout)
设置套接字操作的超时期,timeout是一个浮点数,单位是秒。值为None表示没有超时期。一般,超时期应该在刚创建套接字时设置,因为它们可能用于连接的操作(如 client 连接最多等待5s )
sk.getpeername()
返回连接套接字的远程地址。返回值通常是元组(ipaddr,port)。
sk.getsockname()
返回套接字自己的地址。通常是一个元组(ipaddr,port)
sk.fileno()
套接字的文件描述符
TCP:


2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
2服务端
3
4class Myserver(socketserver.BaseRequestHandler):
5
6 def handle(self):
7
8 conn = self.request
9 conn.sendall(bytes("你好,我是机器人",encoding="utf-8"))
10 while True:
11 ret_bytes = conn.recv(1024)
12 ret_str = str(ret_bytes,encoding="utf-8")
13 if ret_str == "q":
14 break
15 conn.sendall(bytes(ret_str+"你好我好大家好",encoding="utf-8"))
16
17if __name__ == "__main__":
18 server = socketserver.ThreadingTCPServer(("127.0.0.1",8080),Myserver)
19 server.serve_forever()
20
21客户端
22
23import socket
24
25obj = socket.socket()
26
27obj.connect(("127.0.0.1",8080))
28
29ret_bytes = obj.recv(1024)
30ret_str = str(ret_bytes,encoding="utf-8")
31print(ret_str)
32
33while True:
34 inp = input("你好请问您有什么问题? \n >>>")
35 if inp == "q":
36 obj.sendall(bytes(inp,encoding="utf-8"))
37 break
38 else:
39 obj.sendall(bytes(inp, encoding="utf-8"))
40 ret_bytes = obj.recv(1024)
41 ret_str = str(ret_bytes,encoding="utf-8")
42 print(ret_str)
43
案例一 机器人聊天


2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
2
3import socket
4
5sk = socket.socket()
6
7sk.bind(("127.0.0.1",8080))
8sk.listen(5)
9
10while True:
11 conn,address = sk.accept()
12 conn.sendall(bytes("欢迎光临我爱我家",encoding="utf-8"))
13
14 size = conn.recv(1024)
15 size_str = str(size,encoding="utf-8")
16 file_size = int(size_str)
17
18 conn.sendall(bytes("开始传送", encoding="utf-8"))
19
20 has_size = 0
21 f = open("db_new.jpg","wb")
22 while True:
23 if file_size == has_size:
24 break
25 date = conn.recv(1024)
26 f.write(date)
27 has_size += len(date)
28
29 f.close()
30
31客户端
32
33import socket
34import os
35
36obj = socket.socket()
37
38obj.connect(("127.0.0.1",8080))
39
40ret_bytes = obj.recv(1024)
41ret_str = str(ret_bytes,encoding="utf-8")
42print(ret_str)
43
44size = os.stat("yan.jpg").st_size
45obj.sendall(bytes(str(size),encoding="utf-8"))
46
47obj.recv(1024)
48
49with open("yan.jpg","rb") as f:
50 for line in f:
51 obj.sendall(line)
52
案例二 上传文件
UdP


2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
2ip_port = ('127.0.0.1',9999)
3sk = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_DGRAM,0)
4sk.bind(ip_port)
5
6while True:
7 data = sk.recv(1024)
8 print data
9
10
11
12
13import socket
14ip_port = ('127.0.0.1',9999)
15
16sk = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_DGRAM,0)
17while True:
18 inp = input('数据:').strip()
19 if inp == 'exit':
20 break
21 sk.sendto(bytes(inp,encoding = "utf-8"),ip_port)
22
23sk.close()
24
udp传输
WEB服务应用:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
2#coding:utf-8
3import socket
4
5def handle_request(client):
6 buf = client.recv(1024)
7 client.send("HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n\r\n")
8 client.send("Hello, World")
9
10def main():
11 sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
12 sock.bind(('localhost',8080))
13 sock.listen(5)
14
15 while True:
16 connection, address = sock.accept()
17 handle_request(connection)
18 connection.close()
19
20if __name__ == '__main__':
21 main()
22
IO多路复用
I/O(input/output),即输入/输出端口。每个设备都会有一个专用的I/O地址,用来处理自己的输入输出信息首先什么是I/O:
I/O分为磁盘io和网络io,这里说的是网络io
IO多路复用:
I/O多路复用指:通过一种机制,可以监视多个描述符(socket),一旦某个描述符就绪(一般是读就绪或者写就绪),能够通知程序进行相应的读写操作。
Linux
Linux中的 select,poll,epoll 都是IO多路复用的机制。
Linux下网络I/O使用socket套接字来通信,普通I/O模型只能监听一个socket,而I/O多路复用可同时监听多个socket.
I/O多路复用避免阻塞在io上,原本为多进程或多线程来接收多个连接的消息变为单进程或单线程保存多个socket的状态后轮询处理.
Python
Python中有一个select模块,其中提供了:select、poll、epoll三个方法,分别调用系统的 select,poll,epoll 从而实现IO多路复用。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3 提供: select
4
5Mac Python:
6
7 提供: select
8
9Linux Python:
10
11 提供: select、poll、epoll
12
对于select模块操作的方法:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3参数: 可接受四个参数(前三个必须)
4返回值:三个列表
5
6select方法用来监视文件句柄,如果句柄发生变化,则获取该句柄。
71、当 参数1 序列中的句柄发生可读时(accetp和read),则获取发生变化的句柄并添加到 返回值1 序列中
82、当 参数2 序列中含有句柄时,则将该序列中所有的句柄添加到 返回值2 序列中
93、当 参数3 序列中的句柄发生错误时,则将该发生错误的句柄添加到 返回值3 序列中
104、当 超时时间 未设置,则select会一直阻塞,直到监听的句柄发生变化
115、当 超时时间 = 1时,那么如果监听的句柄均无任何变化,则select会阻塞 1 秒,之后返回三个空列表,如果监听的句柄有变化,则直接执行。
12


2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
2import select
3
4
5sk1 = socket.socket()
6sk1.bind(("127.0.0.1",8001))
7sk1.listen()
8
9sk2 = socket.socket()
10sk2.bind(("127.0.0.1",8002))
11sk2.listen()
12
13sk3 = socket.socket()
14sk3.bind(("127.0.0.1",8003))
15sk3.listen()
16
17li = [sk1,sk2,sk3]
18
19while True:
20 r_list,w_list,e_list = select.select(li,[],[],1) # r_list可变化的
21 for line in r_list:
22 conn,address = line.accept()
23 conn.sendall(bytes("Hello World !",encoding="utf-8"))
24
利用select监听终端操作实例


2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
2sk1 = socket.socket()
3sk1.bind(("127.0.0.1",8001))
4sk1.listen()
5
6inpu = [sk1,]
7
8while True:
9 r_list,w_list,e_list = select.select(inpu,[],[],1)
10 for sk in r_list:
11 if sk == sk1:
12 conn,address = sk.accept()
13 inpu.append(conn)
14 else:
15 try:
16 ret = str(sk.recv(1024),encoding="utf-8")
17 sk.sendall(bytes(ret+"hao",encoding="utf-8"))
18 except Exception as ex:
19 inpu.remove(sk)
20
21客户端
22import socket
23
24obj = socket.socket()
25
26obj.connect(('127.0.0.1',8001))
27
28while True:
29 inp = input("Please(q\退出):\n>>>")
30 obj.sendall(bytes(inp,encoding="utf-8"))
31 if inp == "q":
32 break
33 ret = str(obj.recv(1024),encoding="utf-8")
34 print(ret)
35
利用select实现伪同时处理多个Socket客户端请求


2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
2import socket
3sk1 = socket.socket()
4sk1.bind(("127.0.0.1",8001))
5sk1.listen()
6inputs = [sk1]
7import select
8message_dic = {}
9outputs = []
10while True:
11
12 r_list, w_list, e_list = select.select(inputs,[],inputs,1)
13 print("正在监听的socket对象%d" % len(inputs))
14 print(r_list)
15 for sk1_or_conn in r_list:
16 if sk1_or_conn == sk1:
17 conn,address = sk1_or_conn.accept()
18 inputs.append(conn)
19 message_dic[conn] = []
20 else:
21 try:
22 data_bytes = sk1_or_conn.recv(1024)
23 data_str = str(data_bytes,encoding="utf-8")
24 sk1_or_conn.sendall(bytes(data_str+"好",encoding="utf-8"))
25 except Exception as ex:
26 inputs.remove(sk1_or_conn)
27 else:
28 data_str = str(data_bytes,encoding="utf-8")
29 message_dic[sk1_or_conn].append(data_str)
30 outputs.append(sk1_or_conn)
31 for conn in w_list:
32 recv_str = message_dic[conn][0]
33 del message_dic[conn][0]
34 conn.sendall(bytes(recv_str+"好",encoding="utf-8"))
35 for sk in e_list:
36 inputs.remove(sk)
37
38客户端:
39import socket
40
41obj = socket.socket()
42
43obj.connect(('127.0.0.1',8001))
44
45while True:
46 inp = input("Please(q\退出):\n>>>")
47 obj.sendall(bytes(inp,encoding="utf-8"))
48 if inp == "q":
49 break
50 ret = str(obj.recv(1024),encoding="utf-8")
51 print(ret)
52
利用select实现伪同时处理多个Socket客户端请求读写分离
socketserver
 SocketServer内部使用 IO多路复用 以及 “多线程” 和 “多进程” ,从而实现并发处理多个客户端请求的Socket服务端。即:每个客户端请求连接到服务器时,Socket服务端都会在服务器是创建一个“线程”或者“进程” 专门负责处理当前客户端的所有请求。
SocketServer内部使用 IO多路复用 以及 “多线程” 和 “多进程” ,从而实现并发处理多个客户端请求的Socket服务端。即:每个客户端请求连接到服务器时,Socket服务端都会在服务器是创建一个“线程”或者“进程” 专门负责处理当前客户端的所有请求。
ThreadingTCPServer
ThreadingTCPServer实现的Soket服务器内部会为每个client创建一个 “线程”,该线程用来和客户端进行交互。
1、ThreadingTCPServer基础
使用ThreadingTCPServer:
- 创建一个继承自 SocketServer.BaseRequestHandler 的类
- 类中必须定义一个名称为 handle 的方法
- 启动ThreadingTCPServer


2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3class Myserver(socketserver.BaseRequestHandler):
4
5 def handle(self):
6
7 conn = self.request
8 conn.sendall(bytes("你好,我是机器人",encoding="utf-8"))
9 while True:
10 ret_bytes = conn.recv(1024)
11 ret_str = str(ret_bytes,encoding="utf-8")
12 if ret_str == "q":
13 break
14 conn.sendall(bytes(ret_str+"你好我好大家好",encoding="utf-8"))
15
16if __name__ == "__main__":
17 server = socketserver.ThreadingTCPServer(("127.0.0.1",8080),Myserver)
18 server.serve_forever()
19
服务端


2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2
3obj = socket.socket()
4
5obj.connect(("127.0.0.1",8080))
6
7ret_bytes = obj.recv(1024)
8ret_str = str(ret_bytes,encoding="utf-8")
9print(ret_str)
10
11while True:
12 inp = input("你好请问您有什么问题? \n >>>")
13 if inp == "q":
14 obj.sendall(bytes(inp,encoding="utf-8"))
15 break
16 else:
17 obj.sendall(bytes(inp, encoding="utf-8"))
18 ret_bytes = obj.recv(1024)
19 ret_str = str(ret_bytes,encoding="utf-8")
20 print(ret_str)
21
客户端
2、ThreadingTCPServer源码剖析
ThreadingTCPServer的类图关系如下:
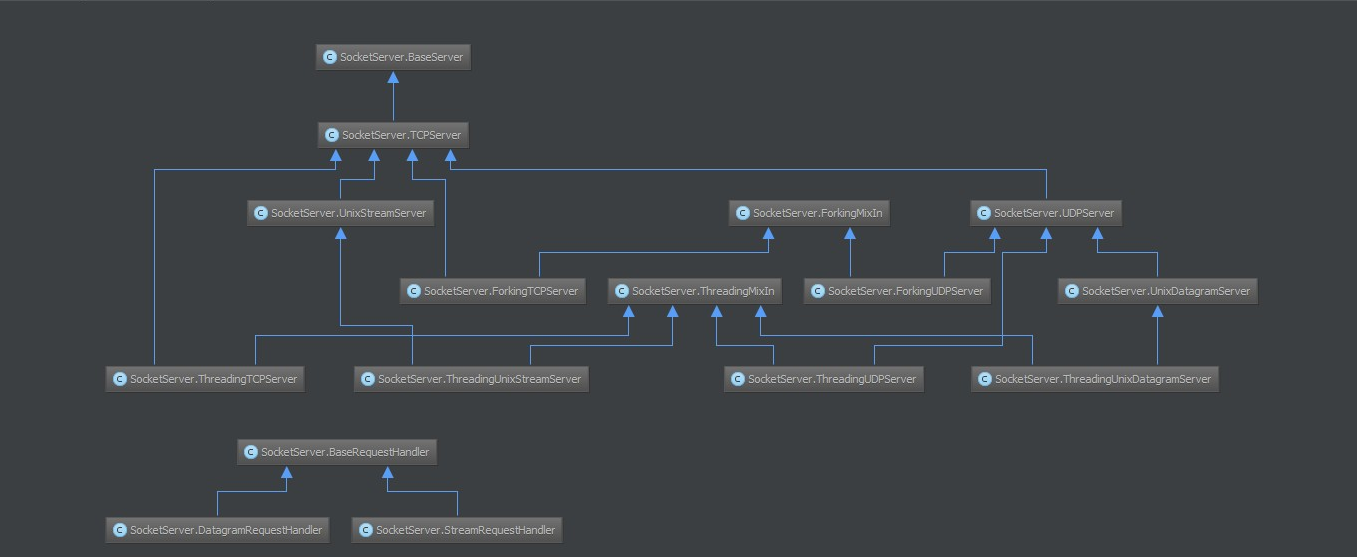
内部调用流程为:
- 启动服务端程序
- 执行 TCPServer.init 方法,创建服务端Socket对象并绑定 IP 和 端口
- 执行 BaseServer.init 方法,将自定义的继承自SocketServer.BaseRequestHandler 的类 MyRequestHandle赋值给 self.RequestHandlerClass
- 执行 BaseServer.server_forever 方法,While 循环一直监听是否有客户端请求到达 …
- 当客户端连接到达服务器
- 执行 ThreadingMixIn.process_request 方法,创建一个 “线程” 用来处理请求
- 执行 ThreadingMixIn.process_request_thread 方法
- 执行 BaseServer.finish_request 方法,执行 self.RequestHandlerClass() 即:执行 自定义 MyRequestHandler 的构造方法(自动调用基类BaseRequestHandler的构造方法,在该构造方法中又会调用 MyRequestHandler的handle方法)
相对应的源码如下:


2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
2
3 """Base class for server classes.
4
5 Methods for the caller:
6
7 - __init__(server_address, RequestHandlerClass)
8 - serve_forever(poll_interval=0.5)
9 - shutdown()
10 - handle_request() # if you do not use serve_forever()
11 - fileno() -> int # for select()
12
13 Methods that may be overridden:
14
15 - server_bind()
16 - server_activate()
17 - get_request() -> request, client_address
18 - handle_timeout()
19 - verify_request(request, client_address)
20 - server_close()
21 - process_request(request, client_address)
22 - shutdown_request(request)
23 - close_request(request)
24 - handle_error()
25
26 Methods for derived classes:
27
28 - finish_request(request, client_address)
29
30 Class variables that may be overridden by derived classes or
31 instances:
32
33 - timeout
34 - address_family
35 - socket_type
36 - allow_reuse_address
37
38 Instance variables:
39
40 - RequestHandlerClass
41 - socket
42
43 """
44
45 timeout = None
46
47 def __init__(self, server_address, RequestHandlerClass):
48 """Constructor. May be extended, do not override."""
49 self.server_address = server_address
50 self.RequestHandlerClass = RequestHandlerClass
51 self.__is_shut_down = threading.Event()
52 self.__shutdown_request = False
53
54 def server_activate(self):
55 """Called by constructor to activate the server.
56
57 May be overridden.
58
59 """
60 pass
61
62 def serve_forever(self, poll_interval=0.5):
63 """Handle one request at a time until shutdown.
64
65 Polls for shutdown every poll_interval seconds. Ignores
66 self.timeout. If you need to do periodic tasks, do them in
67 another thread.
68 """
69 self.__is_shut_down.clear()
70 try:
71 while not self.__shutdown_request:
72 # XXX: Consider using another file descriptor or
73 # connecting to the socket to wake this up instead of
74 # polling. Polling reduces our responsiveness to a
75 # shutdown request and wastes cpu at all other times.
76 r, w, e = _eintr_retry(select.select, [self], [], [],
77 poll_interval)
78 if self in r:
79 self._handle_request_noblock()
80 finally:
81 self.__shutdown_request = False
82 self.__is_shut_down.set()
83
84 def shutdown(self):
85 """Stops the serve_forever loop.
86
87 Blocks until the loop has finished. This must be called while
88 serve_forever() is running in another thread, or it will
89 deadlock.
90 """
91 self.__shutdown_request = True
92 self.__is_shut_down.wait()
93
94 # The distinction between handling, getting, processing and
95 # finishing a request is fairly arbitrary. Remember:
96 #
97 # - handle_request() is the top-level call. It calls
98 # select, get_request(), verify_request() and process_request()
99 # - get_request() is different for stream or datagram sockets
100 # - process_request() is the place that may fork a new process
101 # or create a new thread to finish the request
102 # - finish_request() instantiates the request handler class;
103 # this constructor will handle the request all by itself
104
105 def handle_request(self):
106 """Handle one request, possibly blocking.
107
108 Respects self.timeout.
109 """
110 # Support people who used socket.settimeout() to escape
111 # handle_request before self.timeout was available.
112 timeout = self.socket.gettimeout()
113 if timeout is None:
114 timeout = self.timeout
115 elif self.timeout is not None:
116 timeout = min(timeout, self.timeout)
117 fd_sets = _eintr_retry(select.select, [self], [], [], timeout)
118 if not fd_sets[0]:
119 self.handle_timeout()
120 return
121 self._handle_request_noblock()
122
123 def _handle_request_noblock(self):
124 """Handle one request, without blocking.
125
126 I assume that select.select has returned that the socket is
127 readable before this function was called, so there should be
128 no risk of blocking in get_request().
129 """
130 try:
131 request, client_address = self.get_request()
132 except socket.error:
133 return
134 if self.verify_request(request, client_address):
135 try:
136 self.process_request(request, client_address)
137 except:
138 self.handle_error(request, client_address)
139 self.shutdown_request(request)
140
141 def handle_timeout(self):
142 """Called if no new request arrives within self.timeout.
143
144 Overridden by ForkingMixIn.
145 """
146 pass
147
148 def verify_request(self, request, client_address):
149 """Verify the request. May be overridden.
150
151 Return True if we should proceed with this request.
152
153 """
154 return True
155
156 def process_request(self, request, client_address):
157 """Call finish_request.
158
159 Overridden by ForkingMixIn and ThreadingMixIn.
160
161 """
162 self.finish_request(request, client_address)
163 self.shutdown_request(request)
164
165 def server_close(self):
166 """Called to clean-up the server.
167
168 May be overridden.
169
170 """
171 pass
172
173 def finish_request(self, request, client_address):
174 """Finish one request by instantiating RequestHandlerClass."""
175 self.RequestHandlerClass(request, client_address, self)
176
177 def shutdown_request(self, request):
178 """Called to shutdown and close an individual request."""
179 self.close_request(request)
180
181 def close_request(self, request):
182 """Called to clean up an individual request."""
183 pass
184
185 def handle_error(self, request, client_address):
186 """Handle an error gracefully. May be overridden.
187
188 The default is to print a traceback and continue.
189
190 """
191 print '-'*40
192 print 'Exception happened during processing of request from',
193 print client_address
194 import traceback
195 traceback.print_exc() # XXX But this goes to stderr!
196 print '-'*40
197
Baseserver


2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
2
3 """Base class for various socket-based server classes.
4
5 Defaults to synchronous IP stream (i.e., TCP).
6
7 Methods for the caller:
8
9 - __init__(server_address, RequestHandlerClass, bind_and_activate=True)
10 - serve_forever(poll_interval=0.5)
11 - shutdown()
12 - handle_request() # if you don't use serve_forever()
13 - fileno() -> int # for select()
14
15 Methods that may be overridden:
16
17 - server_bind()
18 - server_activate()
19 - get_request() -> request, client_address
20 - handle_timeout()
21 - verify_request(request, client_address)
22 - process_request(request, client_address)
23 - shutdown_request(request)
24 - close_request(request)
25 - handle_error()
26
27 Methods for derived classes:
28
29 - finish_request(request, client_address)
30
31 Class variables that may be overridden by derived classes or
32 instances:
33
34 - timeout
35 - address_family
36 - socket_type
37 - request_queue_size (only for stream sockets)
38 - allow_reuse_address
39
40 Instance variables:
41
42 - server_address
43 - RequestHandlerClass
44 - socket
45
46 """
47
48 address_family = socket.AF_INET
49
50 socket_type = socket.SOCK_STREAM
51
52 request_queue_size = 5
53
54 allow_reuse_address = False
55
56 def __init__(self, server_address, RequestHandlerClass, bind_and_activate=True):
57 """Constructor. May be extended, do not override."""
58 BaseServer.__init__(self, server_address, RequestHandlerClass)
59 self.socket = socket.socket(self.address_family,
60 self.socket_type)
61 if bind_and_activate:
62 try:
63 self.server_bind()
64 self.server_activate()
65 except:
66 self.server_close()
67 raise
68
69 def server_bind(self):
70 """Called by constructor to bind the socket.
71
72 May be overridden.
73
74 """
75 if self.allow_reuse_address:
76 self.socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
77 self.socket.bind(self.server_address)
78 self.server_address = self.socket.getsockname()
79
80 def server_activate(self):
81 """Called by constructor to activate the server.
82
83 May be overridden.
84
85 """
86 self.socket.listen(self.request_queue_size)
87
88 def server_close(self):
89 """Called to clean-up the server.
90
91 May be overridden.
92
93 """
94 self.socket.close()
95
96 def fileno(self):
97 """Return socket file number.
98
99 Interface required by select().
100
101 """
102 return self.socket.fileno()
103
104 def get_request(self):
105 """Get the request and client address from the socket.
106
107 May be overridden.
108
109 """
110 return self.socket.accept()
111
112 def shutdown_request(self, request):
113 """Called to shutdown and close an individual request."""
114 try:
115 #explicitly shutdown. socket.close() merely releases
116 #the socket and waits for GC to perform the actual close.
117 request.shutdown(socket.SHUT_WR)
118 except socket.error:
119 pass #some platforms may raise ENOTCONN here
120 self.close_request(request)
121
122 def close_request(self, request):
123 """Called to clean up an individual request."""
124 request.close()
125
TCP server


2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
2 """Mix-in class to handle each request in a new thread."""
3
4 # Decides how threads will act upon termination of the
5 # main process
6 daemon_threads = False
7
8 def process_request_thread(self, request, client_address):
9 """Same as in BaseServer but as a thread.
10
11 In addition, exception handling is done here.
12
13 """
14 try:
15 self.finish_request(request, client_address)
16 self.shutdown_request(request)
17 except:
18 self.handle_error(request, client_address)
19 self.shutdown_request(request)
20
21 def process_request(self, request, client_address):
22 """Start a new thread to process the request."""
23 t = threading.Thread(target = self.process_request_thread,
24 args = (request, client_address))
25 t.daemon = self.daemon_threads
26 t.start()
27
ThreadingMixIn


2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
2
3 """Base class for request handler classes.
4
5 This class is instantiated for each request to be handled. The
6 constructor sets the instance variables request, client_address
7 and server, and then calls the handle() method. To implement a
8 specific service, all you need to do is to derive a class which
9 defines a handle() method.
10
11 The handle() method can find the request as self.request, the
12 client address as self.client_address, and the server (in case it
13 needs access to per-server information) as self.server. Since a
14 separate instance is created for each request, the handle() method
15 can define arbitrary other instance variariables.
16
17 """
18
19 def __init__(self, request, client_address, server):
20 self.request = request
21 self.client_address = client_address
22 self.server = server
23 self.setup()
24 try:
25 self.handle()
26 finally:
27 self.finish()
28
29 def setup(self):
30 pass
31
32 def handle(self):
33 pass
34
35 def finish(self):
36 pass
37
SocketServer.BaseRequestHandler
SocketServer的ThreadingTCPServer之所以可以同时处理请求得益于 select 和 Threading 两个东西,其实本质上就是在服务器端为每一个客户端创建一个线程,当前线程用来处理对应客户端的请求,所以,可以支持同时n个客户端链接(长连接)。
