这一部分学习下Dart语法怎么进行IO文件操作。
本身而言,Dart语法进行文件操作是十分简便的,下图是简单写入操作;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3try {
4 File file = new File(filePath);
5 file.writeAsString("$file");
6} catch(e) {
7 print(e);
8}
9
但是往往存在多个文件写入、读取同步、异步的问题,因此这些需要进行考虑;
Directory.create函数是异步模式,返回值是Future
如果要等待函数执行完毕后,再执行之后的代码
那么一般有以下3种方法:
直接调用同步模式函数,如:Directory.createSync
将执行的之后的代码放到then函数中
使用关键字await,外层函数用async声明返回值为Future
举个例子,下面的代码中
fun1、fun2和fun3三个函数结果一样
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
2
3void main(){
4 fun1();
5 fun2();
6 fun3();
7}
8
9void fun1() {
10 var directory = new Directory("temp1");
11 directory.createSync();
12 //absolute返回path为绝对路径的Directory对象
13 print(directory.absolute.path);
14}
15
16void fun2() {
17 new Directory("temp2").create().then(
18 (dir) => print(dir.absolute.path)
19 );
20}
21
22//Dart中变量的类型可以省略,包括函数
23fun3() async {
24 var directory = await new Directory("temp3").create();
25 print(directory.absolute.path);
26}
27
运行结果:
2
3
4
2E:\DartProject\Note16\temp2
3E:\DartProject\Note16\temp3
4
1.针对目录,主要有以下几个操作:
-
创建指定目录
-
重命名目录
-
删除目录
-
创建临时文件夹
-
获取父目录
-
列出目录的内容
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
2import 'dart:async';
3
4void main() {
5 handleDir();
6}
7
8handleDir() async {
9 //可以用Platform.pathSeparator代替路径中的分隔符"/"
10 //效果和"dir/subdir"一样
11 //如果有子文件夹,需要设置recursive: true
12 var directory = await new Directory("dir${Platform.pathSeparator}one").create(recursive: true);
13
14 assert(await directory.exists() == true);
15 //输出绝对路径
16 print("Path: ${directory.absolute.path}");
17
18 //重命名文件夹
19 directory = await directory.rename("dir/subdir");
20 print("Path: ${directory.absolute.path}\n");
21
22 //创建临时文件夹
23 //参数是文件夹的前缀,后面会自动添加随机字符串
24 //参数可以是空参数
25 var tempDir = await Directory.systemTemp.createTemp('temp_dir');
26 assert(await tempDir.exists() == true);
27 print("Temp Path: ${tempDir.path}");
28
29 //返回上一级文件夹
30 var parentDir = tempDir.parent;
31 print("Parent Path: ${parentDir.path}");
32
33 //列出所有文件,不包括链接和子文件夹
34 Stream<FileSystemEntity> entityList = parentDir .list(recursive: false, followLinks: false);
35 await for(FileSystemEntity entity in entityList) {
36
37 //文件、目录和链接都继承自FileSystemEntity
38 //FileSystemEntity.type静态函数返回值为FileSystemEntityType
39 //FileSystemEntityType有三个常量:
40 //Directory、FILE、LINK、NOT_FOUND
41 //FileSystemEntity.isFile .isLink .isDerectory可用于判断类型
42 print(entity.path);
43 }
44
45 //删除目录
46 await tempDir.delete();
47 assert(await tempDir.exists() == false);
48}
49
运行结果:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2Path: E:\DartProject\Note16\dir/subdir
3
4Temp Path: C:\Users\King\AppData\Local\Temp\temp_dir7aa9c6f5-106b-11e6-a55f-ac220b7553ea
5Parent Path: C:\Users\King\AppData\Local\Temp
6C:\Users\King\AppData\Local\Temp\%@DH19{R%DFDKB85J)D~UR6.png
7C:\Users\King\AppData\Local\Temp\0RCT3Y_IOUNT2`)27FJ9U`R.xml
8C:\Users\King\AppData\Local\Temp\360newstmp.dat
9……
10
2.针对文件,主要有以下几个操作:
-
创建文件
-
将string写入文件
-
读取文件到String
-
以行为单位读取文件到List<String>
-
将bytes写入文件
-
读取文件到bytes
-
数据流Stream写入文件
-
数据流Stream读取文件
-
删除文件
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
2import 'dart:convert';
3import 'dart:async';
4
5void main() {
6 //文件操作演示
7 handleFile();
8}
9
10handleFile() async {
11 //提示:pub中有ini库可以方便的对ini文件进行解析
12 File file = new File("default.ini");
13
14 //如果文件存在,删除
15 if(!await file.exists()) {
16 //创建文件
17 file = await file.create();
18 }
19
20 print(file);
21
22 //直接调用File的writeAs函数时
23 //默认文件打开方式为WRITE:如果文件存在,会将原来的内容覆盖
24 //如果不存在,则创建文件
25
26 //写入String,默认将字符串以UTF8进行编码
27 file = await file.writeAsString("[General]\nCode=UTF8");
28 //readAsString读取文件,并返回字符串
29 //默认返回的String编码为UTF8
30 //相关的编解码器在dart:convert包中
31 //包括以下编解码器:ASCII、LANTI1、BASE64、UTF8、SYSTEM_ENCODING
32 //SYSTEM_ENCODING可以自动检测并返回当前系统编码
33 print("\nRead Strings:\n${await file.readAsString()}");
34
35 //以行为单位读取文件到List<String>,默认为UTF8编码
36 print("\nRead Lines:");
37 List<String> lines = await file.readAsLines();
38 lines.forEach(
39 (String line) => print(line)
40 );
41
42 //如果是以字节方式写入文件
43 //建议设置好编码,避免汉字、特殊符号等字符出现乱码、或无法读取
44 //将字符串编码为Utf8格式,然后写入字节
45 file = await file.writeAsBytes(UTF8.encode("编码=UTF8"));
46 //读取字节,并用Utf8解码
47 print("\nRead Bytes:");
48 print(UTF8.decode(await file.readAsBytes()));
49
50// //删除文件
51// await file.delete();
52}
53
运行结果:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
2
3Read Strings:
4[General]
5Code=UTF8
6
7Read Lines:
8[General]
9Code=UTF8
10
11Read Bytes:
12编码=UTF8
13
读写文件的话,常用的函数就是readAs和writeAs
但是如果我们要对某个字符进行处理,或读写某个区域等操作时
就需要用到open函数
open类型的函数有3个:
open({FileMode mode: FileMode.READ}) → Future<RandomAccessFile>
openRead([int start, int end]) → Stream<List<int>>
openWrite({FileMode mode: FileMode.WRITE, Encoding encoding: UTF8}) → IOSink
open和openSync一样,不过一个是异步、一个同步
可以返回RandomAccessFile类
openRead用于打开数据流
openWrite用于打开数据缓冲池
详细的内容可以查看API
3.针对链接,主要有以下几个操作:
-
创建链接
-
获取链接文件的路径
-
获取链接指向的目标
-
重命名链接
-
删除链接
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
2import 'dart:async';
3
4void main() {
5 handleLink();
6}
7
8handleLink() async {
9 //创建文件夹
10 var dir = await new Directory("linkDir").create();
11 //创建链接
12 //Link的参数为该链接的Path,create的参数为链接的目标文件夹
13 var link = await new Link("shortcut").create("linkDir");
14
15 //输出链接文件的路径
16 print(link.path);
17 //输出链接目标的路径
18 print(await link.target());
19
20 //重命名链接
21 link = await link.rename("link");
22 print(link.path);
23
24 //删除链接
25 //link.delete();
26}
27
运行结果:
2
3
4
2E:\DartProject\Note16\linkDir
3link
4
需要说明的是,Dart中的Link
链接的是文件夹,而不能链接文件
并且,Dart中的链接和通常意义的快捷方式不同:
- 首先,这里的链接只能指向文件夹
快捷方式可以指向文件夹或文件
- 链接不能剪切移动
快捷方式可以剪切移动
- 在命令行中,链接可以作为普通文件夹进行 cd、dir(ls)等操作
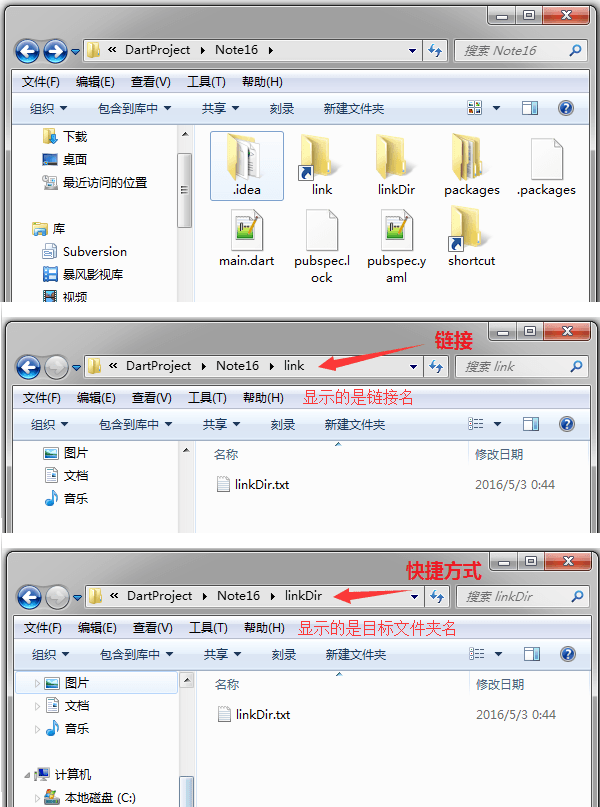
快捷方式在命令行中可以看到,只是一个lnk文件,运行然后打开目标资源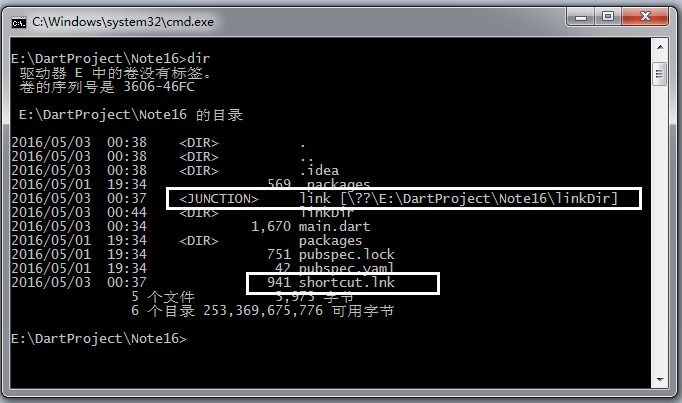
- 打开链接的时候,资源管理器的地址栏显示的是链接名
而快捷方式打开的时候,资源管理器显示的是目标文件夹名
4.针对数据流,主要有以下几个操作:
原本是准备在文件操作一节中提一下就完事的
但是测试了解下来,有点复杂,于是单独列一节
Stream是dart:async库中的类,并非dart:io
从它的位置可以看出,Stream是一个异步数据事件的提供者
它提供了一种接收事件序列(数据或错误信息)的方式
因此,我们可以通过listen来监听并开始产生事件
当我们开始监听Stream的时候,会接收到一个StreamSubscription对象
通过该对象可以控制Stream进行暂停、取消等操作
数据流Stream有两种类型:
- Single-subscription单一订阅数据流
- broadcast广播数据流
Stream默认关闭广播数据流,可以通过isBroadcast测试
如果要打开,需在Stream子类中重写 isBroadcast返回true
或调用asBroadcastStream
Single-subscription对象不能监听2次
即使第1次的数据流已经被取消
同时,为了保证系统资源被释放
在使用数据流的时候
必须等待读取完数据,或取消
关于数据流Stream,虽然抽象,但也不是不能理解
问题在于很多人不知道【Dart中】数据流的好处,何时该用
我所理解的是一般用于处理较大的连续数据,如文件IO操作
下面的实例是用数据流来复制文件,只能算是抛砖引玉吧!
File.copy常用来复制文件到某路径,但是看不到复制的过程、进度
这里用Stream来实现复制文件的功能,并添加进度显示的功能
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
2import 'dart:convert';
3import 'dart:async';
4
5void main() {
6 //复制文件演示
7 copyFileByStream();
8}
9
10copyFileByStream() async {
11 //电子书文件大小:10.9 MB (11,431,697 字节)
12 File file = new File(r"E:\全职高手.txt");
13 assert(await file.exists() == true);
14 print("源文件:${file.path}");
15
16 //以只读方式打开源文件数据流
17 Stream<List<int>> inputStream = file.openRead();
18 //数据流监听事件,这里onData是null
19 //会在后面通过StreamSubscription来修改监听函数
20 StreamSubscription subscription = inputStream.listen(null);
21
22 File target = new File(r"E:\全职高手.back.txt");
23 print("目标文件:${target.path}");
24 //以WRITE方式打开文件,创建缓存IOSink
25 IOSink sink = target.openWrite();
26
27 //常用两种复制文件的方法,就速度来说,File.copy最高效
28// //经测试,用时21毫秒
29// await file.copy(target.path);
30// //输入流连接缓存,用时79毫秒,比想象中高很多
31// //也许是数据流存IOSink缓存中之后,再转存到文件中的原因吧!
32// await sink.addStream(inputStream);
33
34 //手动处理输入流
35 //接收数据流的时候,涉及一些简单的计算
36 //如:当前进度、当前时间、构造字符串
37 //但是最后测试下来,仅用时68毫秒,有些不可思议
38
39 //文件大小
40 int fileLength = await file.length();
41 //已读取文件大小
42 int count = 0;
43 //模拟进度条
44 String progress = "*";
45
46 //当输入流传来数据时,设置当前时间、进度条,输出信息等
47 subscription.onData((List<int> list) {
48 count = count + list.length;
49 //进度百分比
50 double num = (count*100)/fileLength;
51 DateTime time = new DateTime.now();
52
53 //输出样式:[1:19:197]**********[20.06%]
54 //进度每传输2%,多一个"*"
55 //复制结束进度为100%,共50个"*"
56 print("[${time.hour}:${time.second}:${time.millisecond}]${progress*(num ~/ 2)}[${num.toStringAsFixed(2)}%]");
57
58 //将数据添加到缓存池
59 sink.add(list);
60 });
61
62 //数据流传输结束时,触发onDone事件
63 subscription.onDone(() {
64 print("复制文件结束!");
65 //关闭缓存释放系统资源
66 sink.close();
67 });
68}
69
运行结果:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2目标文件:E:\全职高手.back.txt
3[1:19:177][0.57%]
4[1:19:185][1.15%]
5[1:19:186][1.72%]
6[1:19:187]*[2.29%]
7[1:19:187]*[2.87%]
8……
9[1:19:245]*************************************************[99.75%]
10[1:19:245]**************************************************[100.00%]
11复制文件结束!
12
本文图片资料来源出自“Dart语言中文社区”,允许转载,转载时请务必以超链接形式标明文章原始出处 。
