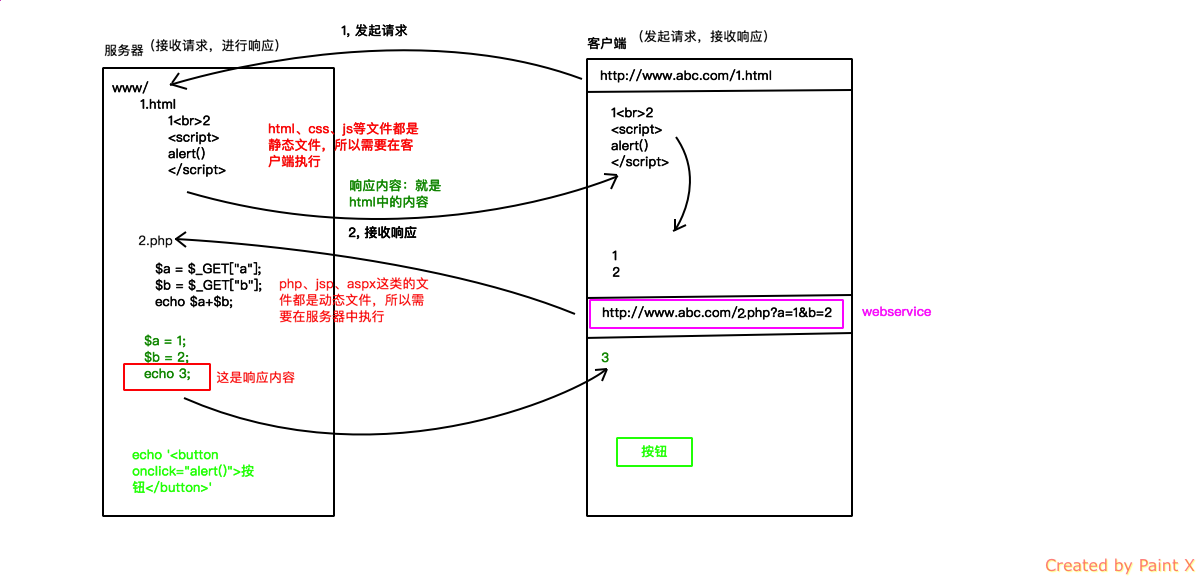
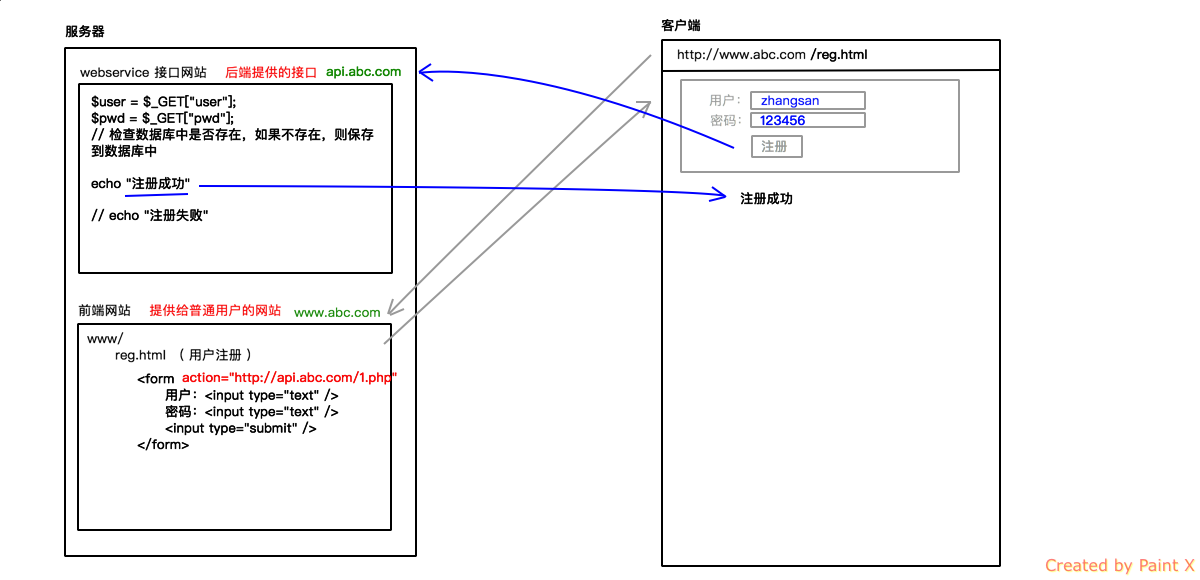
什么是nodejs?
-
Node.js 是一个基于 Chrome V8 引擎的 JavaScript 运行环境。
-
Node.js 使用了一个事件驱动、非阻塞式 I/O 的模型,使其轻量又高效。
-
Node.js 的包管理器 npm,是全球最大的开源库生态系统。
nodejs 编写及运行
一:打开终端:windows-开始-运行-cmd
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2测试服务器是否支持node环境:node -v 回车
3进入node环境:node 回车
4编写代码:function sum(a,b){return a+b} sum(3,7) 回车之后,终端中就会显示sum运行后的结果10
5
6不好的地方:代码不能长时间保存
7
8退出:从node环境退回到命令行环境
9 连续两次 ctrl+c
10
11
二:编写一个.js文件,在该文件中,编写js代码,在终端中执行这个文件
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2c:/users/wangyang/1.js
3 ```
4 function sum(a, b){
5 return a+b;
6 }
7
8 console.log( sum(1,2) )
9 ```
10在终端中,执行 node 1.js,前提是命令行必须在wangyang目录下,然后通过 node 1.js 才能找到对应的文件。
11
12如果不在同一个文件夹中
13
141, node abc/1.js
15
162, cd abc
17 node 1.js
18
19
重启服务
js文件编写好了之后,在终端中执行 node app.js 能够挂起服务,如果修改app.js文件,需要重启服务才能让修改后的代码起作用,如果重启服务
2
3
4
2node app.js // 启动服务 node app 也可以省略文件扩展名,简写启动服务
3
4
热部署工具
-
在开发时,代码是需要经常修改的,但是修改后是无法直接访问的,必须重启服务才行。所以采用热部署工具,让代码修改后,服务器能够自动重启,这样就减轻了我们的工作。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3自动重启的方法:
4
5 npm install nodemon –g
6 nodemon app.js
7
8 npm install supervisors –g
9 supervisors app.js
10
11
http 模块
-
http模块创建网站服务
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2 http.createServer(function (request, response) {
3 // 发送 HTTP 头部
4 response.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html;charset=utf-8'});
5 // IP地址
6 console.log(request.connection.remoteAddress);
7 // 发送响应数据
8 response.end('Hello World');
9 }).listen(8080);
10
11
-
http路由:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2http.createServer(function (request, response) {
3 response.writeHead(200,{
4 'Content-Type':'text/html;charset=utf-8',
5 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin':'*'
6 });
7 console.log(request.url);
8 response.end();
9}).listen(8080);
10
11
12
-
接收GET数据:
2
3
2
3
-
接收POST数据:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2 request.on('data', function(chunk){
3 post += chunk;
4 });
5 request.on('end', function(){
6 post = require("querystring").parse(post); // {a:1,b:2}
7 });
8
9
- 模块化开发:
如果所有的代码都写在同一个js文件中,那么会导致文件越来越大,所以我们可以采用模块化的写法,把代码分离出来。
- 建立模块
比如我们做一个sum.js文件,里面写入:
module.exports = function(a, b){return a+b}
- 使用模块
var sum = require("./sum"); // 载入sum.js文件
sum(1, 2); // 3
NodeJS 属于 CommonJS 规范,可以理解成用 exports 输出模块,用 require 引入模块。
express模块
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2// npm install express
3
4// step2: 引入express模块
5const express = require("express");
6
7// step3: 使用模块
8const app = express(); // 获取express对象,这个对象提供了很多功能
9
10// 开发一个网站站点
11// 定义一个路由规则
12// app.get("/", callback回调函数) 语义指用户使用get方式请求我们网站的根目录时,执行callback回调函数
13app.get("/", function(req, res){ // req指请求(request) res指响应(response)
14 console.log(req.ip, "访问了服务器");
15 res.send("这是首页"+ req.ip.substring(7) +"访问了这个页面");
16})
17
18app.listen(8080); // 监听8080端口 65535以内
19
20
21
get 参数
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
2 const url = require("url"); // 系统模块,无需install
3
4 http.createServer(function(req, res){
5 res.writeHead(200, {
6 "content-type":"text/html;charset=utf-8"
7 });
8
9 //console.log(req.url);
10 let router = url.parse(req.url, true);
11 let query = router.query;
12
13 if( router.pathname === "/" ){
14 res.end(`
15 <form method="get" action="/chk">
16 用户名:<input type="text" name="username" /><br>
17 密码:<input type="text" name="password" /><br>
18 <input type="submit" value="提交" />
19 </form>
20 `);
21 }else if( router.pathname === "/chk" ){
22 res.write( query.username+"<br>"+query.password );
23 res.end();
24 }else{
25 res.end("其他的请求");
26 }
27 }).listen(8080);
28
29
post 参数
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
2const http = require("http");
3const url = require("url");
4const querystring = require("querystring");
5
6http.createServer(function(req, res){
7 // 中文乱码和html解析
8 res.writeHead(200, {
9 "content-type":"text/html;charset=utf-8"
10 });
11 // 路由规则
12 let router = url.parse(req.url, true);
13
14 switch( router.pathname ){
15 case "/":
16 res.end(`
17 <form method="post" action="/chk">
18 用户名:<input type="text" name="username" /><br>
19 密码:<input type="text" name="password" /><br>
20 <input type="submit" value="提交" />
21 </form>
22 `);
23 break;
24 case "/chk":
25 // 监听 post 数据
26 // 得到一部分请求中的数据时,就执行的回调函数
27 var chunks = "";
28 //req.on(data)指每次发送的数据;
29 req.on("data", function( chunk ){
30 //console.log( chunk.toString() )
31 chunks += chunk;
32 });
33 //req.on(end)数据发送完成;
34 req.on("end", function(){
35 //console.log(chunks)
36 //console.log( querystring.parse(chunks) )
37 //console.log( querystring.stringify({ username: "123", password: "456456" }) )
38 var body = querystring.parse(chunks);
39 //console.log( body.username );
40 res.write( body.username+"<br>"+body.password );
41 res.end("处理");
42 })
43
44
45 break;
46 default:
47 res.end("");
48 }
49
50}).listen(8080);
51
52
53
什么是后端?什么是前后端分离?什么是webservice?什么是路由?如何接收请求中的数据?如何模块化开发?