1 添加redis支持
在pom.xml中添加
Xml代码
- <
dependency
<
groupId
org.springframework.boot
</
groupId
<
artifactId
spring-boot-starter-redis
</
artifactId
</
dependency
2 redis配置
Java代码
- package com.wisely.ij.config;
- import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
- import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
- import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
- import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
- import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport;
- import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
- import org.springframework.cache.interceptor.KeyGenerator;
- import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
- import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
- import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
- import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
- import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
- import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
- import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
- import java.lang.reflect.Method;
- @Configuration
- @EnableCaching
- public
class RedisConfig
extends CachingConfigurerSupport{
@Bean
public KeyGenerator wiselyKeyGenerator(){
return
new KeyGenerator() {
@Override
public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object… params) {
- StringBuilder sb =
new StringBuilder();
- sb.append(target.getClass().getName());
- sb.append(method.getName());
for (Object obj : params) {
- sb.append(obj.toString());
- }
return sb.toString();
- }
- };
- }
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(
@SuppressWarnings(
"rawtypes") RedisTemplate redisTemplate) {
return
new RedisCacheManager(redisTemplate);
- }
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate(
- RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
- StringRedisTemplate template =
new StringRedisTemplate(factory);
- Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer =
new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.
class);
- ObjectMapper om =
new ObjectMapper();
- om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
- om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
- jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
- template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
- template.afterPropertiesSet();
return template;
- }
- }
3 redis服务器配置
Properties代码
- # REDIS (RedisProperties)
- spring.redis.database= # database name
- spring.redis.host=localhost # server host
- spring.redis.password= # server password
- spring.redis.port=
6379 # connection port
- spring.redis.pool.max-idle=
8 # pool settings …
- spring.redis.pool.min-idle=
0
- spring.redis.pool.max-active=
8
- spring.redis.pool.max-wait=-
1
- spring.redis.sentinel.master= # name of Redis server
- spring.redis.sentinel.nodes= # comma-separated list of host:port pairs
4 应用
测试两个实体类
Java代码
- package com.wisely.ij.domain;
- public
class Address {
private Long id;
private String province;
private String city;
public Address(Long id,String province, String city) {
this.id = id;
this.province = province;
this.city = city;
- }
public Address() {
- }
public Long getId() {
return id;
- }
public
void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
- }
public String getProvince() {
return province;
- }
public
void setProvince(String province) {
this.province = province;
- }
public String getCity() {
return city;
- }
public
void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
- }
- }
Java代码
- package com.wisely.ij.domain;
- public
class User {
private Long id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
public User(Long id,String firstName, String lastName) {
this.id = id ;
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
- }
public User() {
- }
public Long getId() {
return id;
- }
public
void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
- }
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
- }
public
void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
- }
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
- }
public
void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
- }
- }
使用演示
Java代码
- package com.wisely.ij.service;
- import com.wisely.ij.domain.Address;
- import com.wisely.ij.domain.User;
- import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
- import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
- /**
- * Created by wisely on 2015/5/25.
- */
- @Service
- public
class DemoService {
@Cacheable(value =
"usercache",keyGenerator =
"wiselyKeyGenerator")
public User findUser(Long id,String firstName,String lastName){
- System.out.println(
"无缓存的时候调用这里");
return
new User(id,firstName,lastName);
- }
@Cacheable(value =
"addresscache",keyGenerator =
"wiselyKeyGenerator")
public Address findAddress(Long id,String province,String city){
- System.out.println(
"无缓存的时候调用这里");
return
new Address(id,province,city);
- }
- }
Java代码
- package com.wisely.ij.web;
- import com.wisely.ij.domain.Address;
- import com.wisely.ij.domain.User;
- import com.wisely.ij.service.DemoService;
- import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
- import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
- /**
- * Created by wisely on 2015/5/25.
- */
- @Controller
- public
class DemoController {
@Autowired
- DemoService demoService;
@RequestMapping(
"/test")
@ResponseBody
public String putCache(){
- demoService.findUser(1l,
"wang",
"yunfei");
- demoService.findAddress(1l,
"anhui",
"hefei");
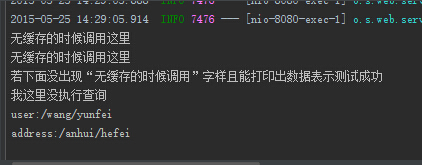
- System.out.println(
"若下面没出现“无缓存的时候调用”字样且能打印出数据表示测试成功");
return
"ok";
- }
@RequestMapping(
"/test2")
@ResponseBody
public String testCache(){
- User user = demoService.findUser(1l,
"wang",
"yunfei");
- Address address =demoService.findAddress(1l,
"anhui",
"hefei");
- System.out.println(
"我这里没执行查询");
- System.out.println(
"user:"+
"/"+user.getFirstName()+
"/"+user.getLastName());
- System.out.println(
"address:"+
"/"+address.getProvince()+
"/"+address.getCity());
return
"ok";
- }
- }
5 检验
先访问http://localhost:8080/test 保存缓存
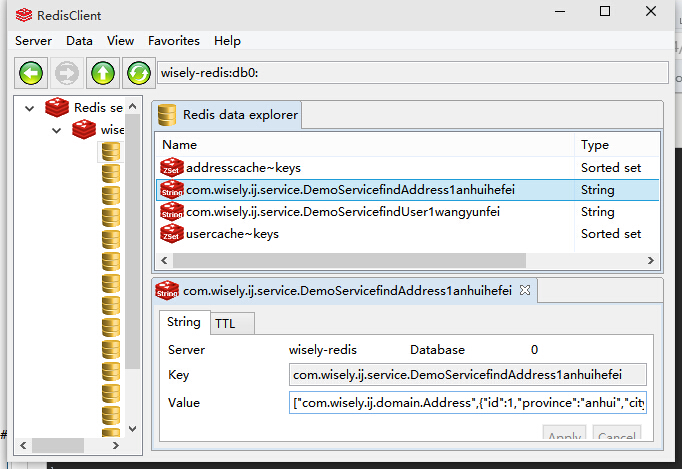
再访问http://localhost:8080/test2 调用缓存里的数据
http://wiselyman.iteye.com/blog/2184884
《整合 spring 4(包括mvc、context、orm) + mybatis 3 示例》一文简要介绍了最新版本的 Spring MVC、IOC、MyBatis ORM 三者的整合以及声明式事务处理。现在我们需要把缓存也整合进来,缓存我们选用的是 Redis,本文将在该文示例基础上介绍 Redis 缓存 + Spring 的集成。关于 Redis 服务器的搭建请参考博客《Redhat5.8 环境下编译安装 Redis 并将其注册为系统服务》。
1. 依赖包安装
pom.xml 加入:
[html] view plain
copy
print?
- <!– redis cache related…..start –>
- <
dependency
<
groupId
org.springframework.data
</
groupId
<
artifactId
spring-data-redis
</
artifactId
<
version
1.6.0.RELEASE
</
version
- </
dependency
- <
dependency
<
groupId
redis.clients
</
groupId
<
artifactId
jedis
</
artifactId
<
version
2.7.3
</
version
- </
dependency
- <!– redis cache related…..end –>
2. Spring 项目集成进缓存支持
要启用缓存支持,我们需要创建一个新的 CacheManager bean。CacheManager 接口有很多实现,本文演示的是和 Redis 的集成,自然就是用 RedisCacheManager 了。Redis 不是应用的共享内存,它只是一个内存服务器,就像 MySql 似的,我们需要将应用连接到它并使用某种“语言”进行交互,因此我们还需要一个连接工厂以及一个 Spring 和 Redis 对话要用的 RedisTemplate,这些都是 Redis 缓存所必需的配置,把它们都放在自定义的 CachingConfigurerSupport 中:
[java] view plain
copy
print?
- /**
- * File Name:RedisCacheConfig.java
- *
- * Copyright Defonds Corporation 2015
- * All Rights Reserved
- *
- */
- package com.defonds.bdp.cache.redis;
- import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
- import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport;
- import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
- import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
- import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
- import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
- import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
- import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory;
- import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
- /**
- *
- * Project Name:bdp
- * Type Name:RedisCacheConfig
- * Type Description:
- * Author:Defonds
- * Create Date:2015-09-21
- *
- * @version
- *
- */
- @Configuration
- @EnableCaching
- public
class RedisCacheConfig
extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
@Bean
public JedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() {
- JedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory =
new JedisConnectionFactory();
// Defaults
- redisConnectionFactory.setHostName(
"192.168.1.166");
- redisConnectionFactory.setPort(
6379);
return redisConnectionFactory;
- }
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory cf) {
- RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate =
new RedisTemplate<String, String>();
- redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(cf);
return redisTemplate;
- }
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisTemplate redisTemplate) {
- RedisCacheManager cacheManager =
new RedisCacheManager(redisTemplate);
// Number of seconds before expiration. Defaults to unlimited (0)
- cacheManager.setDefaultExpiration(
3000);
// Sets the default expire time (in seconds)
return cacheManager;
- }
- }
当然也别忘了把这些 bean 注入 Spring,不然配置无效。在 applicationContext.xml 中加入以下:
[html] view plain
copy
print?
- <
context:component-scan
base-package=
"com.defonds.bdp.cache.redis"
/>
3. 缓存某些方法的执行结果
设置好缓存配置之后我们就可以使用 @Cacheable 注解来缓存方法执行的结果了,比如根据省份名检索城市的 provinceCities 方法和根据 city_code 检索城市的 searchCity 方法:
[java] view plain
copy
print?
- // R
- @Cacheable(
"provinceCities")
- public List<City> provinceCities(String province) {
- logger.debug(
"province=" + province);
return
this.cityMapper.provinceCities(province);
- }
- // R
- @Cacheable(
"searchCity")
- public City searchCity(String city_code){
- logger.debug(
"city_code=" + city_code);
return
this.cityMapper.searchCity(city_code);
- }
4. 缓存数据一致性保证
CRUD (Create 创建,Retrieve 读取,Update 更新,Delete 删除) 操作中,除了 R 具备幂等性,其他三个发生的时候都可能会造成缓存结果和数据库不一致。为了保证缓存数据的一致性,在进行 CUD 操作的时候我们需要对可能影响到的缓存进行更新或者清除。
[java] view plain
copy
print?
- // C
- @CacheEvict(value = {
"provinceCities"}, allEntries =
true)
- public
void insertCity(String city_code, String city_jb,
- String province_code, String city_name,
- String city, String province) {
- City cityBean =
new City();
- cityBean.setCityCode(city_code);
- cityBean.setCityJb(city_jb);
- cityBean.setProvinceCode(province_code);
- cityBean.setCityName(city_name);
- cityBean.setCity(city);
- cityBean.setProvince(province);
this.cityMapper.insertCity(cityBean);
- }
- // U
- @CacheEvict(value = {
"provinceCities",
"searchCity" }, allEntries =
true)
- public
int renameCity(String city_code, String city_name) {
- City city =
new City();
- city.setCityCode(city_code);
- city.setCityName(city_name);
this.cityMapper.renameCity(city);
return
1;
- }
- // D
- @CacheEvict(value = {
"provinceCities",
"searchCity" }, allEntries =
true)
- public
int deleteCity(String city_code) {
this.cityMapper.deleteCity(city_code);
return
1;
- }
业务考虑,本示例用的都是 @CacheEvict 清除缓存。如果你的 CUD 能够返回 City 实例,也可以使用 @CachePut 更新缓存策略。笔者推荐能用 @CachePut 的地方就不要用 @CacheEvict,因为后者将所有相关方法的缓存都清理掉,比如上面三个方法中的任意一个被调用了的话,provinceCities 方法的所有缓存将被清除。
5. 自定义缓存数据 key 生成策略
对于使用 @Cacheable 注解的方法,每个缓存的 key 生成策略默认使用的是参数名+参数值,比如以下方法:
[java] view plain
copy
print?
- @Cacheable(
"users")
- public User findByUsername(String username)
这个方法的缓存将保存于 key 为 users~keys 的缓存下,对于 username 取值为 "赵德芳" 的缓存,key 为 "username-赵德芳"。一般情况下没啥问题,二般情况如方法 key 取值相等然后参数名也一样的时候就出问题了,如:
[java] view plain
copy
print?
- @Cacheable(
"users")
- public Integer getLoginCountByUsername(String username)
这个方法的缓存也将保存于 key 为 users~keys 的缓存下。对于 username 取值为 "赵德芳" 的缓存,key 也为 "username-赵德芳",将另外一个方法的缓存覆盖掉。
解决办法是使用自定义缓存策略,对于同一业务(同一业务逻辑处理的方法,哪怕是集群/分布式系统),生成的 key 始终一致,对于不同业务则不一致:
[java] view plain
copy
print?
- @Bean
- public KeyGenerator customKeyGenerator() {
return
new KeyGenerator() {
@Override
public Object generate(Object o, Method method, Object… objects) {
- StringBuilder sb =
new StringBuilder();
- sb.append(o.getClass().getName());
- sb.append(method.getName());
for (Object obj : objects) {
- sb.append(obj.toString());
- }
return sb.toString();
- }
- };
- }
于是上述两个方法,对于 username 取值为 "赵德芳" 的缓存,虽然都还是存放在 key 为 users~keys 的缓存下,但由于 key 分别为 "类名-findByUsername-username-赵德芳" 和 "类名-getLoginCountByUsername-username-赵德芳",所以也不会有问题。
这对于集群系统、分布式系统之间共享缓存很重要,真正实现了分布式缓存。
笔者建议:缓存方法的 @Cacheable 最好使用方法名,避免不同的方法的 @Cacheable 值一致,然后再配以以上缓存策略。
6. 缓存的验证
6.1 缓存的验证
为了确定每个缓存方法到底有没有走缓存,我们打开了 MyBatis 的 SQL 日志输出,并且为了演示清楚,我们还清空了测试用 Redis 数据库。
先来验证 provinceCities 方法缓存,Eclipse 启动 tomcat 加载项目完毕,使用 JMeter 调用 /bdp/city/province/cities.json 接口:
Eclipse 控制台输出如下:
说明这一次请求没有命中缓存,走的是 db 查询。JMeter 再次请求,Eclipse 控制台输出:
标红部分以下是这一次请求的 log,没有访问 db 的 log,缓存命中。查看本次请求的 Redis 存储情况:
同样可以验证 city_code 为 1492 的 searchCity 方法的缓存是否有效:
图中标红部分是 searchCity 的缓存存储情况。
6.2 缓存一致性的验证
先来验证 insertCity 方法的缓存配置,JMeter 调用 /bdp/city/create.json 接口:
之后看 Redis 存储:
可以看出 provinceCities 方法的缓存已被清理掉,insertCity 方法的缓存奏效。
然后验证 renameCity 方法的缓存配置,JMeter 调用 /bdp/city/rename.json 接口:
之后再看 Redis 存储:
searchCity 方法的缓存也已被清理,renameCity 方法的缓存也奏效。
7. 注意事项
- 要缓存的 Java 对象必须实现 Serializable 接口,因为 Spring 会将对象先序列化再存入 Redis,比如本文中的 com.defonds.bdp.city.bean.City 类,如果不实现 Serializable 的话将会遇到类似这种错误:nested exception is java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: DefaultSerializer requires a Serializable payload but received an object of type [com.defonds.bdp.city.bean.City]]。
- 缓存的生命周期我们可以配置,然后托管 Spring CacheManager,不要试图通过 redis-cli 命令行去管理缓存。比如 provinceCities 方法的缓存,某个省份的查询结果会被以 key-value 的形式存放在 Redis,key 就是我们刚才自定义生成的 key,value 是序列化后的对象,这个 key 会被放在 key 名为 provinceCities
keys key-value 存储中,参考下图"provinceCities 方法在 Redis 中的缓存情况"。可以通过 redis-cli 使用 del 命令将 provinceCitieskeys 删除,但每个省份的缓存却不会被清除。 - CacheManager 必须设置缓存过期时间,否则缓存对象将永不过期,这样做的原因如上,避免一些野数据“永久保存”。此外,设置缓存过期时间也有助于资源利用最大化,因为缓存里保留的永远是热点数据。
- 缓存适用于读多写少的场合,查询时缓存命中率很低、写操作很频繁等场景不适宜用缓存。
后记
本文完整 Eclipse 下的开发项目示例已上传 CSDN 资源,有兴趣的朋友可以去下载下来参考:http://download.csdn.net/detail/defonds/9137505。
参考资料
- Caching Data with Spring
-
- Cache Abstraction Part VII. Integration
- Caching Data in Spring Using Redis
- Caching with Spring Data Redis
- spring-redis-caching-example
-
http://blog.csdn.net/defonds/article/details/48716161
本文介绍了如何使用注解的方式,将Redis缓存整合到你的Spring项目。
首先我们将使用jedis驱动,进而开始配置我们的Gradle。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
2version '1.0-SNAPSHOT'
3apply plugin: 'java'
4apply plugin: 'eclipse'
5apply plugin: 'idea'
6apply plugin: 'spring-boot'
7buildscript {
8 repositories {
9 mavenCentral()
10 }
11 dependencies {
12 classpath("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-gradle-plugin:1.2.5.RELEASE")
13 }
14}
15jar {
16 baseName = 'gs-serving-web-content'
17 version = '0.1.0'
18}
19sourceCompatibility = 1.8
20repositories {
21 mavenCentral()
22}
23dependencies {
24 compile "org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf"
25 compile 'org.slf4j:slf4j-api:1.6.6'
26 compile 'ch.qos.logback:logback-classic:1.0.13'
27 compile 'redis.clients:jedis:2.7.0'
28 compile 'org.springframework.data:spring-data-redis:1.5.0.RELEASE'
29 testCompile group: 'junit', name: 'junit', version: '4.11'
30}
31task wrapper(type: Wrapper) {
32 gradleVersion = '2.3'
33}
34
紧接着我们将使用Spring注解,继续执行Redis装载配置。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
2import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
3import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport;
4import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
5import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
6import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
7import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
8import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
9import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory;
10import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
11import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
12import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
13@Configuration
14@EnableCaching
15public class RedisConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
16 @Bean
17 public JedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() {
18 JedisConnectionFactory jedisConnectionFactory = new JedisConnectionFactory();
19 jedisConnectionFactory.setUsePool(true);
20 return jedisConnectionFactory;
21 }
22 @Bean
23 public RedisSerializer redisStringSerializer() {
24 StringRedisSerializer stringRedisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
25 return stringRedisSerializer;
26 }
27 @Bean(name="redisTemplate")
28 public RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory cf,RedisSerializer redisSerializer) {
29 RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<String, String>();
30 redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(cf);
31 redisTemplate.setDefaultSerializer(redisSerializer);
32 return redisTemplate;
33 }
34 @Bean
35 public CacheManager cacheManager() {
36 return new RedisCacheManager(redisTemplate(redisConnectionFactory(),redisStringSerializer()));
37 }
38}
39
下一步将创建缓存接口CacheService。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2import java.util.Date;
3import java.util.List;
4public interface CacheService {
5 public void addMessage(String user,String message);
6 public List<String> listMessages(String user);
7}
8
当然用户既可以增加一条消息也能取回一条消息。因此,在实现过程中,用户相关信息的存在时间将默认设为一分钟。
我们用Redis来继承实现CacheService接口。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
2import com.gkatzioura.spring.cache.CacheService;
3import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ListOperations;
4import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisOperations;
5import org.springframework.data.redis.core.SetOperations;
6import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
7import javax.annotation.Resource;
8import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
9import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
10import java.util.Date;
11import java.util.List;
12@Service("cacheService")
13public class RedisService implements CacheService {
14 @Resource(name = "redisTemplate")
15 private ListOperations<String, String> messageList;
16 @Resource(name = "redisTemplate")
17 private RedisOperations<String,String> latestMessageExpiration;
18 @Override
19 public void addMessage(String user,String message) {
20 messageList.leftPush(user,message);
21 ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = ZonedDateTime.now();
22 Date date = Date.from(zonedDateTime.plus(1, ChronoUnit.MINUTES).toInstant());
23 latestMessageExpiration.expireAt(user,date);
24 }
25 @Override
26 public List<String> listMessages(String user) {
27 return messageList.range(user,0,-1);
28 }
29}
30
我们的缓存机制将保留每个用户发送的消息列表。为了实现这个功能我们将调用ListOperations接口,同时将每个user作为一个key键值。通过RedisOperations接口,我们可以为key设置特定存在时长。在本例中,主要使用的是 user key。
下一步我们将创建一个controller注入缓存服务。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2import com.gkatzioura.spring.cache.CacheService;
3import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
4import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
5import java.util.List;
6@RestController
7public class MessageController {
8 @Autowired
9 private CacheService cacheService;
10 @RequestMapping(value = "/message",method = RequestMethod.GET)
11 @ResponseBody
12 public List<String> greeting(String user) {
13 List<String> messages = cacheService.listMessages(user);
14 return messages;
15 }
16 @RequestMapping(value = "/message",method = RequestMethod.POST)
17 @ResponseBody
18 public String saveGreeting(String user,String message) {
19 cacheService.addMessage(user,message);
20 return "OK";
21 }
22}
23
最后完成类Application的创建。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
3import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
4@SpringBootApplication
5public class Application {
6 public static void main(String[] args) {
7 SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
8 }
9}
10
经过如上步骤,接下来直接运行Application即可。
**原文链接:**Integrate Redis into a Spring Project( 译者/丘志鹏 审校/朱正贵 责编/仲浩)
http://www.csdn.net/article/2015-09-01/2825600
使用Spring Cache + Redis + Jackson Serializer缓存数据库查询结果中序列化问题的解决
应用场景
我们希望通过缓存来减少对关系型数据库的查询次数,减轻数据库压力。在执行DAO类的select***(), query***()方法时,先从Redis中查询有没有缓存数据,如果有则直接从Redis拿到结果,如果没有再向数据库发起查询请求取数据。
序列化问题
要把domain object做为key-value对保存在redis中,就必须要解决对象的序列化问题。Spring Data Redis给我们提供了一些现成的方案:
- JdkSerializationRedisSerializer. 使用JDK提供的序列化功能。 优点是反序列化时不需要提供类型信息(class),但缺点是序列化后的结果非常庞大,是JSON格式的5倍左右,这样就会消耗redis服务器的大量内存。
- Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer. 使用Jackson库将对象序列化为JSON字符串。优点是速度快,序列化后的字符串短小精悍。
但缺点也非常致命,那就是此类的构造函数中有一个类型参数,必须
提供要序列化对象的类型信息(.class对象)。 通过查看源代码,发现其只在反序列化过程中用到了类型信息。
如果用方案一,就必须付出缓存多占用4倍内存的代价,实在承受不起。如果用方案二,则必须给每一种domain对象都配置一个Serializer,即如果我的应用里有100种domain对象,那就必须在spring配置文件中配置100个Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer,这显然是不现实的。
通过google, 发现spring data redis项目中有一个#145 pull request, 而这个提交请求的内容正是解决Jackson必须提供类型信息的问题。然而不幸的是这个请求还没有被merge。但我们可以把代码copy一下放到自己的项目中:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
2 * @author Christoph Strobl
3 * @since 1.6
4 */
5public class GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer implements RedisSerializer<Object> {
6
7 private final ObjectMapper mapper;
8
9 /**
10 * Creates {@link GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer} and configures {@link ObjectMapper} for default typing.
11 */
12 public GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer() {
13 this((String) null);
14 }
15
16 /**
17 * Creates {@link GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer} and configures {@link ObjectMapper} for default typing using the
18 * given {@literal name}. In case of an {@literal empty} or {@literal null} String the default
19 * {@link JsonTypeInfo.Id#CLASS} will be used.
20 *
21 * @param classPropertyTypeName Name of the JSON property holding type information. Can be {@literal null}.
22 */
23 public GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer(String classPropertyTypeName) {
24
25 this(new ObjectMapper());
26
27 if (StringUtils.hasText(classPropertyTypeName)) {
28 mapper.enableDefaultTypingAsProperty(DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL, classPropertyTypeName);
29 } else {
30 mapper.enableDefaultTyping(DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL, As.PROPERTY);
31 }
32 }
33
34 /**
35 * Setting a custom-configured {@link ObjectMapper} is one way to take further control of the JSON serialization
36 * process. For example, an extended {@link SerializerFactory} can be configured that provides custom serializers for
37 * specific types.
38 *
39 * @param mapper must not be {@literal null}.
40 */
41 public GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer(ObjectMapper mapper) {
42
43 Assert.notNull(mapper, "ObjectMapper must not be null!");
44 this.mapper = mapper;
45 }
46
47 /*
48 * (non-Javadoc)
49 * @see org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer#serialize(java.lang.Object)
50 */
51 @Override
52 public byte[] serialize(Object source) throws SerializationException {
53
54 if (source == null) {
55 return SerializationUtils.EMPTY_ARRAY;
56 }
57
58 try {
59 return mapper.writeValueAsBytes(source);
60 } catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
61 throw new SerializationException("Could not write JSON: " + e.getMessage(), e);
62 }
63 }
64
65 /*
66 * (non-Javadoc)
67 * @see org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer#deserialize(byte[])
68 */
69 @Override
70 public Object deserialize(byte[] source) throws SerializationException {
71 return deserialize(source, Object.class);
72 }
73
74 /**
75 * @param source can be {@literal null}.
76 * @param type must not be {@literal null}.
77 * @return {@literal null} for empty source.
78 * @throws SerializationException
79 */
80 public <T> T deserialize(byte[] source, Class<T> type) throws SerializationException {
81
82 Assert.notNull(type,
83 "Deserialization type must not be null! Pleaes provide Object.class to make use of Jackson2 default typing.");
84
85 if (SerializationUtils.isEmpty(source)) {
86 return null;
87 }
88
89 try {
90 return mapper.readValue(source, type);
91 } catch (Exception ex) {
92 throw new SerializationException("Could not read JSON: " + ex.getMessage(), ex);
93 }
94 }
95}
96
然后在配置文件中使用这个GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer:
2
3
2 </bean>
3
重新构建部署,我们发现这个serializer可以同时支持多种不同类型的domain对象,问题解决。
http://www.myexception.cn/database/1958643.html
spring-data-redis提供了多种serializer策略,这对使用jedis的开发者而言,实在是非常便捷。sdr提供了4种内置的serializer:
- JdkSerializationRedisSerializer:使用JDK的序列化手段(serializable接口,ObjectInputStrean,ObjectOutputStream),数据以字节流存储
- StringRedisSerializer:字符串编码,数据以string存储
- JacksonJsonRedisSerializer:json格式存储
- OxmSerializer:xml格式存储
其中JdkSerializationRedisSerializer和StringRedisSerializer是最基础的序列化策略,其中“JacksonJsonRedisSerializer”与“OxmSerializer”都是基于stirng存储,因此它们是较为“高级”的序列化(最终还是使用string解析以及构建java对象)。
RedisTemplate中需要声明4种serializer,默认为“JdkSerializationRedisSerializer”:
1) keySerializer :对于普通K-V操作时,key采取的序列化策略
2) valueSerializer:value采取的序列化策略
3) hashKeySerializer: 在hash数据结构中,hash-key的序列化策略
4) hashValueSerializer:hash-value的序列化策略
无论如何,建议key/hashKey采用StringRedisSerializer。
接下来,通过实例描述如何使用它们,可以首先参考“spring-data-redis特性”:
http://shift-alt-ctrl.iteye.com/blog/1887370
http://www.cnblogs.com/google4y/p/3535106.html
